Stork Enamine Reaction
Stork Enamine Reaction
Enamine is the nitrogen derivative of an enol. Enamine acts as a selective nucleophile. Following figure depicts the carbanion character showed by an enamine.
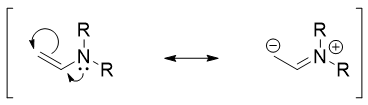
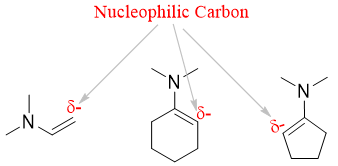
Thus, in enamine the alpha carbons have higher electron densities making it nucleophilic in nature. They are stronger nucleophiles than enols and quite selective in alkylation reactions.
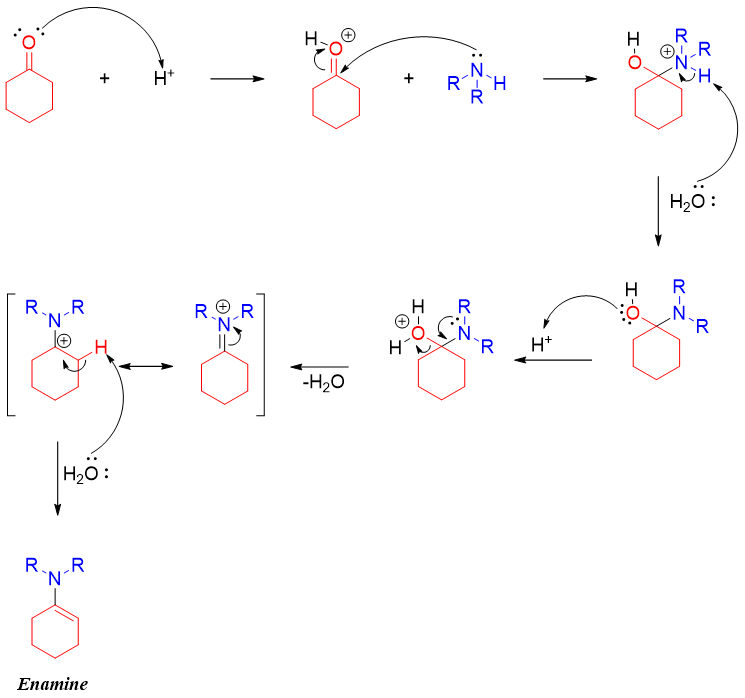
Enamines are formed by reacting secondary amines with aldehydes or ketones. Unlike primary amines which produces imines upon condensation with carbonyl compounds, secondary amines produce enamine after the abstraction of alpha hydrogen of carbonyl compounds. The reaction of secondary amines and carbonyl compound is carried out in Dean-Stark apparatus to remove the water formed during the reaction. Water molecules are also removed using molecular sieves. Following mechanism shows the formation of enamine from secondary amines.
Enamines upon reaction with reactive alkyl halides produce alkylated iminium salts. The iminium salts are unreactive towards further acylation or alkylation reactions. For example,
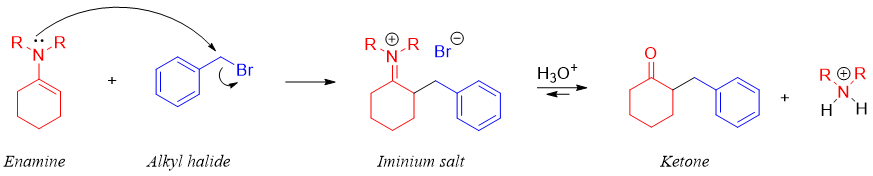
The iminium salt upon hydrolysis produces alkylated ketone. The mechanism of hydrolysis is shown below.
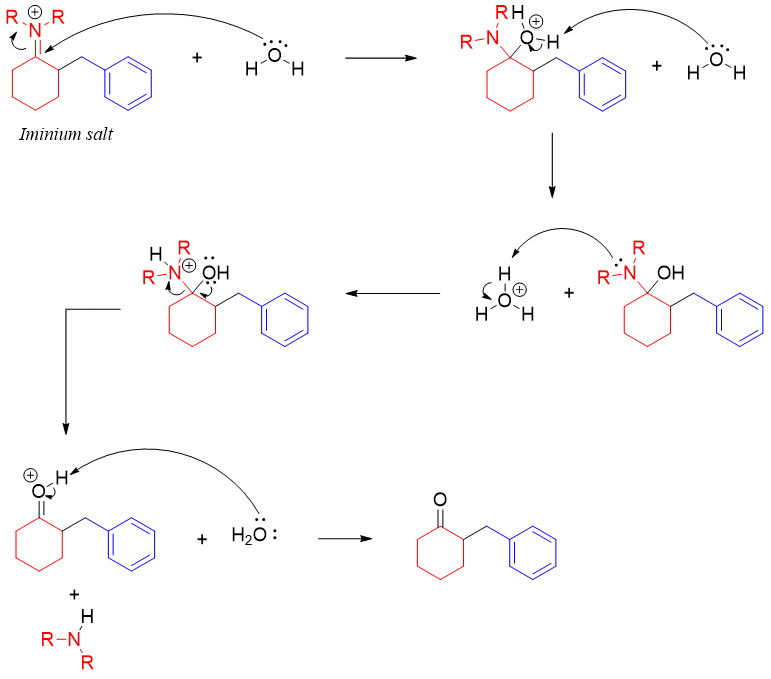
Following are some examples of Stork enamine reaction employed in forming carbon-carbon bond between different molecules.
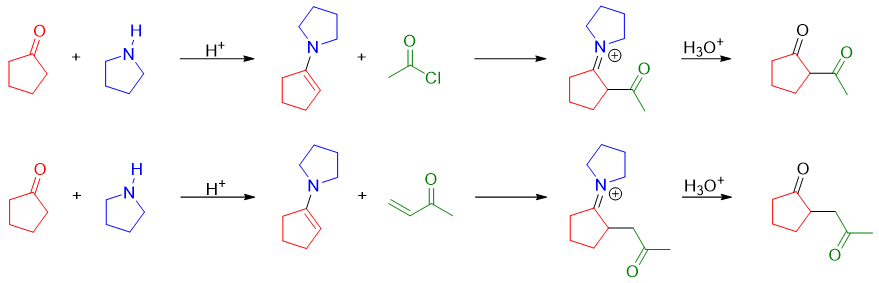
Thus, we can conclude Stork enamine rection is employed for the substitution of alpha proton of carbonyl compound without using any base. The carbonyl compounds arereacted with secondary amine to produce an enamine. Enamine further reacts with alkyl halides or undergo conjugate addition to form new carbon-carbon bond. After that the carbonyl group is regenerated by hydrolysis.
