Cope Elimination
Cope Elimination
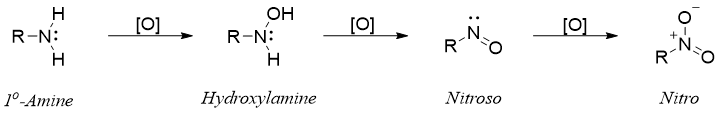
Amines are easy to oxidize when reacted with oxidizing agent. Due to this amines are often stored in air free systems. Sometimes amines or amine containing drugs are protected from oxidation by converting them to their salts. Common oxidizing agents used for the oxidation of amines are hydrogen peroxide, peroxyacids, and permanganate. All three classes of amines produce different oxidation products. Primary amines upon oxidation produces mixture of products. Following scheme shows the oxidation intermediates and products of primary imines.
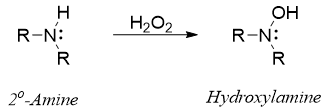
Secondary amines often produce hydroxylamine as a major oxidation product.
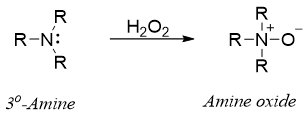
Tertiary amines upon oxidation produces amine oxides as a major product.
The amine oxide formed by the oxidation of tertiary amines can undergo an elimination reaction in which the amine oxide act itself as a base and produces alkenes. This elimination reaction is called as Cope elimination reaction. Same as Hofmann elimination, Cope elimination also produces less substituted alkenes as the major product.
The mechanism of Cope elimination constitutes a single concerted E2 reaction in which the amine oxide acts as a base and leaving group simultaneously.
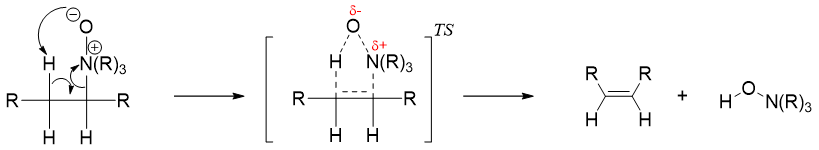
The complete reaction mechanism of Cope elimination reaction is as following.
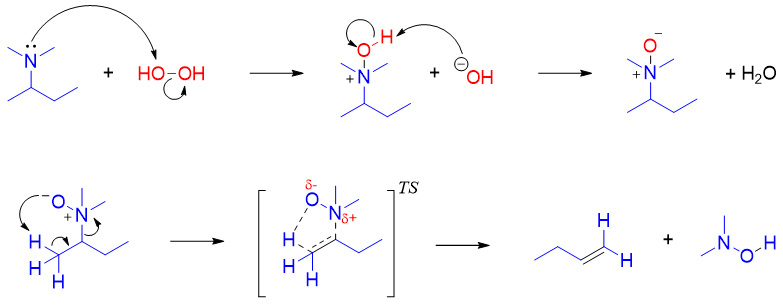
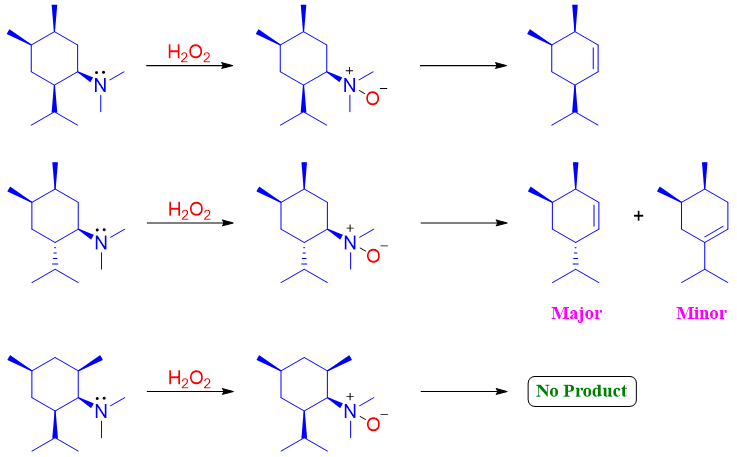
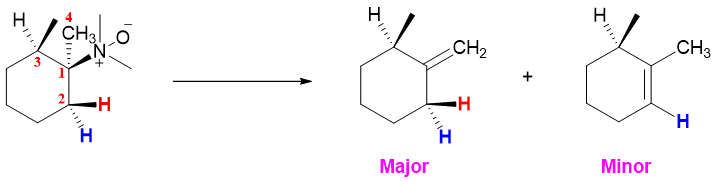
Unlike E2 elimination reactions of alkyl halides, the Cope elimination reaction takes place in syn orientation instead of anti-orientation. The oxygen atom containing negative charge acts as a base while the hydrogens at syn position on next carbon acts as acidic protons. In following molecule there are three protons present at carbon next to carbon at which N-oxide is present. The proton at carbon 3 is not abstracted because this proton is not syn oriented to the N-oxime. The abstraction of proton (red) present at carbon 2 is positioned syn to the N-oxime therefore, it is abstracted. The protons present on carbon 4 can also be abstracted as one of them can get syn orientation any time. Therefore, two products are possible in cope elimination of this molecule. The major product is the one in which both criteria of cope elimination are fulfilled. 1) The acidic proton must be syn to the N-oxide, 2) the final alkene product should be least substituted. Whereas, in the minor product only one criterion of syn orientation is obeyed.
Unlike Hofmann elimination, Cope elimination takes place under mild conditions. For this purpose, this reaction is used in the synthesis of reactive or sensitive alkenes. Following are some examples of Cope elimination reaction.