Diazonium Salts
Diazonium Salts
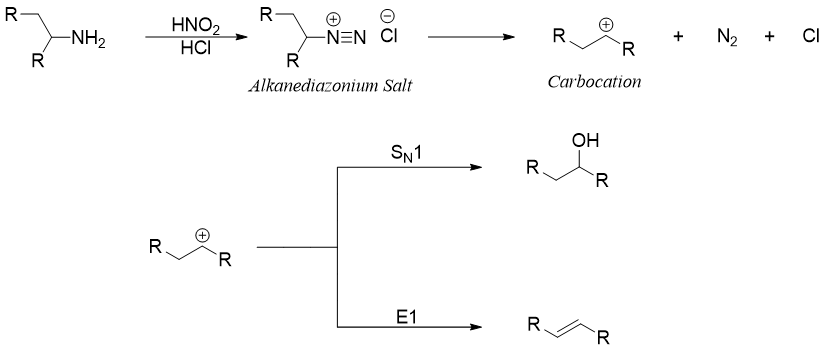
Diazonium salts are group of organic compounds which contains R–[N2]+X- as a functional group. Where R can by an alkyl, or an aryl and X can be an anion particularly a halide.
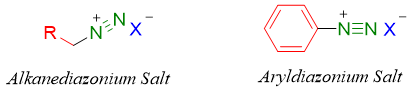
Diazonium salts containing aliphatic alkyl chains are unimportant as they are highly unstable and extremely reactive towards nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions.
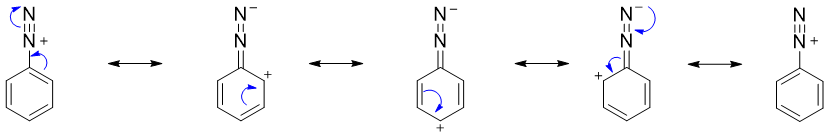
The arenediazonium salts are stable than the alkanediazonium salts. This stability is due to the dispersal of positive charge over the benzene ring through resonance.
Diazonium salts are prepared by reacting primary amines with nitrous acid. Nitrous acid upon reaction with acid produces nitrosonium ion which is the active electrophile attacked by amine nitrogen atom to produce diazonium salts. Nitrous acid is prepared in situ as it is very reactive and hence very unstable. Thus, it is prepared from sodium nitrite.
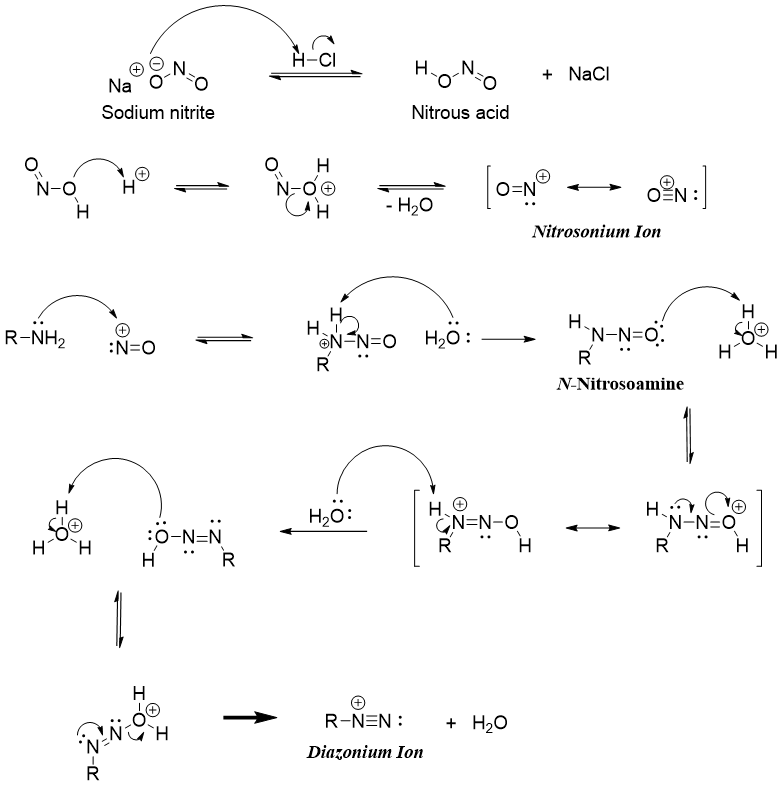
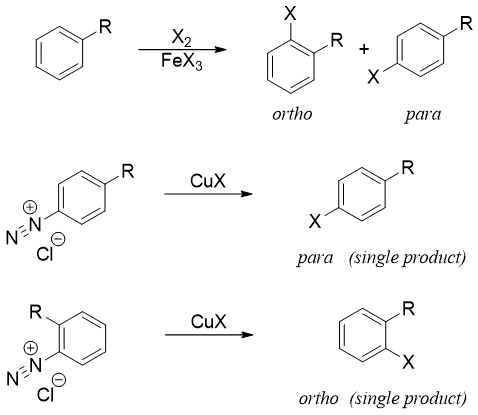
Diazonium salts are very reactive towards attacking nucleophiles. The -N2+ group can be substituted by different nucleophiles. Following scheme depicts some examples.
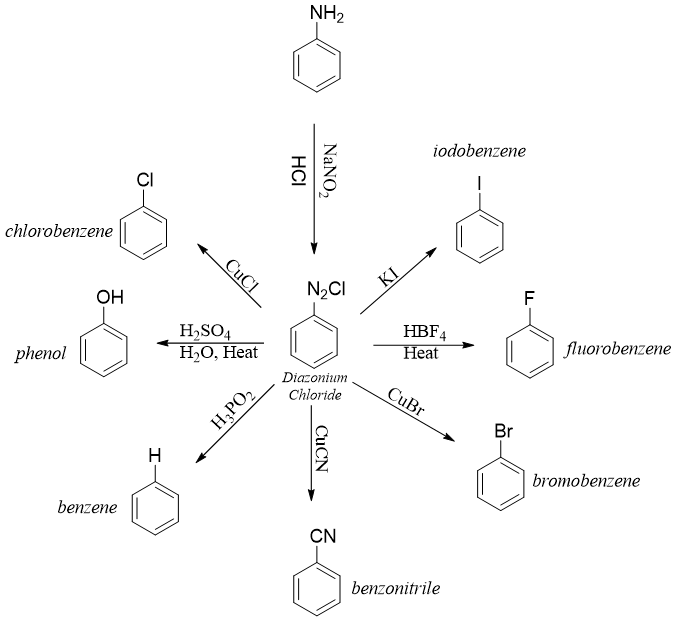
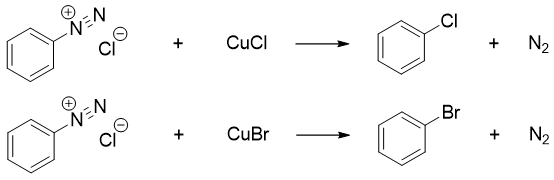
Arydiazonium salts are converted to corresponding aryl halide by reacting it with CuX where X = Cl, Br etc. Such reactions are also known as Sandmeyer reactions.
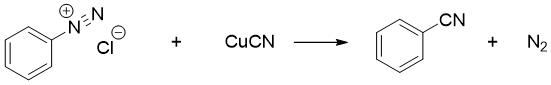
The copper salt in Sandmeyer reaction can also be CuCN to produce benzonitrile.
The synthesis of bromobenzene and chlorobenzene via diazonium salts only produces mono substituted product. Whereas direct chlorination or bromination can yield different products.
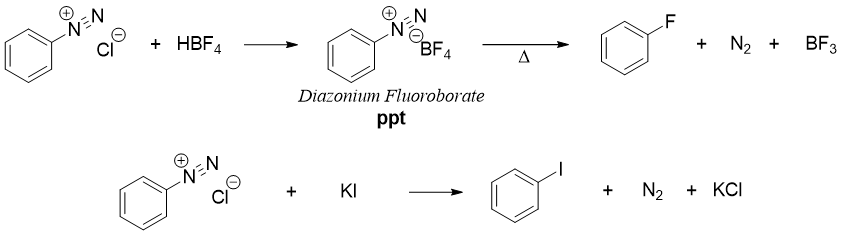
Synthesis of fluorobenzene and iodobenzene is not carried out with Sandmeyer reaction. Fluorobenzene and iodobenzene are synthesized from diazonium salts by reacting it with fluoroboric acid (HBF4) and potassium iodide (KI) respectively.
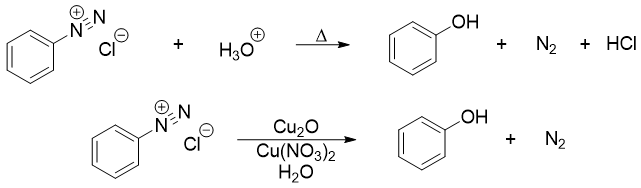
Diazonium salts are converted into phenols by reacting it with water in the presence of an acid. Reacting diazonium salts with aqueous Cu2O and Cu(NO3)2 at lower temperatures produces phenols with higher yields.
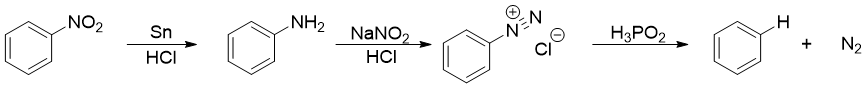
When arenediazonium salt is treated with hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2), the diazonium group will be replaced by hydrogen atom.
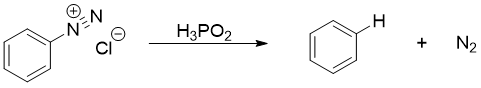
The conversion of arenediazonium salt to benzene is very important reaction for the removal of amino group or nitro group from benzene ring. In synthesis, amino and nitro groups are often placed to direct the incoming substituents on benzene ring. Once their role is completed, they can be removed by converting them into diazonium salt and then treating them with H3PO2 to substitute it with hydrogen atom.