Nomenclature of Alkenes
NOMENCLATURE OF ALKENES
Alkenes are compounds that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. This is a family of unsaturated hydrocarbons with the molecular formula of CnH2n. Because of the number of alkene compounds possible, a systematic way of naming these compounds was developed.
Nomenclature of alkenes follows same general naming rules for alkanes, except, the suffix –ane for alkanes is replaced by –ene. Important differences in the naming system includes:
- The parent chain needs not to be the longest possible carbon chain.
- The number of double bonds is considered in naming the compound.
- The position of the unsaturation site is also included in the name.
These few differences make naming alkenes slightly more complicated. The specific steps in naming alkenes are as follows:
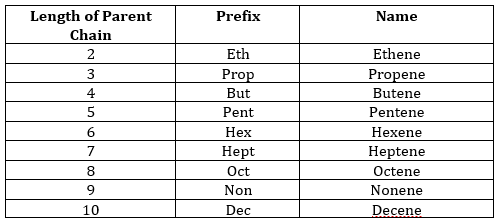
- 1. Name the parent compound by identifying the longest carbon chain that contains the maximum number of double bonds. Use the following prefix and add –ene in the end:
- 2. Number the carbons of the parent chain so the double bond will have the lowest possible numbers.
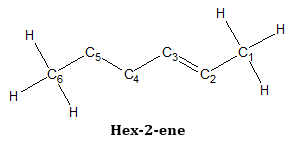
The double bond is nearest the carbon the right most of the structure and so that carbon will be labeled one. The number labels for each carbon is shown in the figure.
- 3. If the double bond is equidistant from both ends, number the chain giving the lowest possible number to the first substituent.
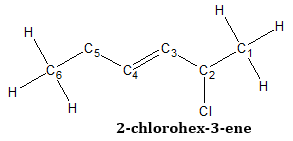
Since the double bond is equidistant from both ends, the basis for numbering is the substituent closest one end of the chain. Since there is only one substituent which is the chloro group, and it is nearer the carbon in the right most of the chain, numbering starts with that carbon.
- 4. Write out the full name, numbering the substituents according to their position in the chain and list them in alphabetical order.
- 5. Indicate the double bond by the number of the first carbon of the C=C bond.
- 6. If more than one double bond is present, indicate the position of the double bond by using the number of the first carbon of each double bond and use the suffix –diene (if there are two double bonds), -triene (for three double bonds), -tetraene (for four double bonds), etc.
- 7. If there two or more chains competing for selection as the parent chain (chain with the most multiple bonds), the choice goes to the chain with the greatest number of carbon atoms.
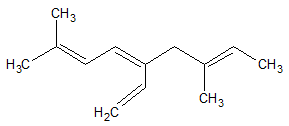
As can be seen in the compound, there are two possible chains that would contain both three double bonds. However, the chain inside the blue box in the image below has more carbon atoms in its chain. Because of that, the chain in the box will be considered the parent chain.
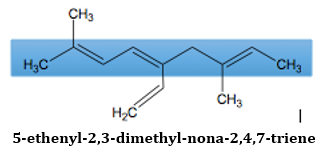
- 8. When alkenes are considered as substituents, name the compounds using the rules above and replace the suffix –ene with –enyl.
