Hydrogenation of Alkenes
HYDROGENATION OF ALKENES
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing one or more carbon-carbon double bond. Each of these double bonds contains a sigma bond and a pi bond. Pi bonds are relatively weaker compared to sigma bonds. Because of the presence of these pi bonds, alkenes are more reactive than alkanes that contain only sigma bonds. Because of these, reagents can be added to an alkene to break the pi bond between carbon atoms, and replace them with two sigma bonds on each of the carbon atoms.
One common example of an addition reaction in alkene is hydrogenation. Hydrogenation reactions involve addition of hydrogen atoms across the carbon-carbon double bond. The resulting product of this reaction is a saturated alkane. The process of hydrogenation is thermodynamically favored because the product formed by the reaction is a lower energy product (more stable).
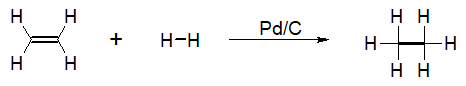
Since this type of reaction involves formation of a lower energy product, the reaction is considered to be exothermic. This means that during hydrogenation, energy is released in the form of heat. Even though a thermodynamically favored product is formed, this specific reaction needs a catalyst for it to proceed. Without the catalyst, the high activation energy requirement makes hydrogenation a difficult reaction to proceed.
There are a number of catalysts that are commonly used in the hydrogenation process of alkenes. These catalysts include platinum oxide (PtO2), palladium-graphite (Pd-C), and radium –nickel (Ra-Ni). The presence of these catalysts allows an alternative mechanism for the reaction that requires lesser amounts of energy for it to proceed.
In catalytic hydrogenation, the hydrogen molecule (H-H) attaches itself to the metal surface to produce metal-hydrogen (M-H) bonds. At the same time, alkenes also adsorb on the surface of the metal forming carbon-metal (C-M) bonds. With proper orientation, a hydrogen atom may transfer to the alkene to form new C-H bond. Another H atom can attach itself to the other carbon atom to form another C-H single bond. Every time a hydrogen atom attaches itself to a carbon atom in the double bond, the C-M bond for that carbon atom is removed. In the process, when two H atoms already attached through the original C=C, the resulting alkane will be free from C-M bonds and are eventually released from the surface of the catalyst.

Since, the new C-H bonds only replaced the C-M bonds, addition of the hydrogen atoms are said to be syn each other. This means they are added on the same side of the carbon-carbon double bond.
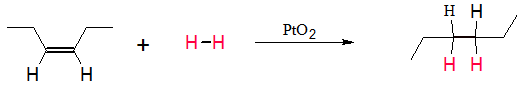
Hydrogenation reactions are important processes in the food industry. Spreads and shortening agents are prepared by hydrogenating oils. The process of hydrogenation can be used to increase the chemical stability of products. In the coal industry, solid coal is also converted to liquid by hydrogenation. Liquid coal are the ones used as fuel in several industries.
