General Introduction
Introduction
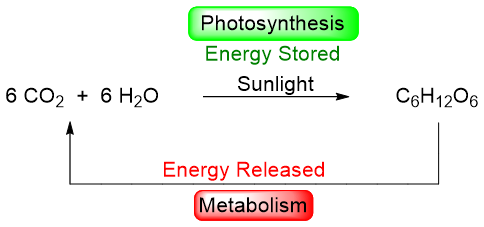
Carbohydrates are the most abundant bioorganic compounds present in almost every living organism. The name carbohydrate is derived from two words: carbon and hydrate (water). Hence, the general molecular formula of carbohydrate is Cn(H2O)n. Examples of pure carbohydrates include starch and sugar present in food, cotton, and paper. Carbohydrates are the main storehouses of energy. In plants and algae carbohydrates are synthesized by the process of photosynthesis. In photosynthesis the sunlight is used by the green plant to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen molecules. The amount of energy absorbed during the glucose formation is released when the glucose is metabolized.
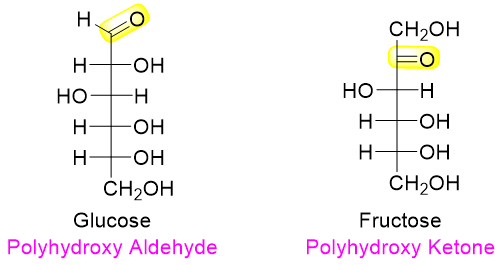
The carbohydrates are either polyhydroxy ketones like fructose, polyhydroxy aldehydes like glucose, or compounds made up of many polyhydroxy ketones or polyhydroxy aldehydes linked together. The chemical structures of carbohydrates are represented by Fischer projections. Following are the Fischer projections of fructose and glucose. Both compounds have the same molecular formula C6H12O6.
Carbohydrates are one of the major sources of energy in all living organisms. In plants the main source of energy is the starch. Starch is the polysaccharide made up of glucose monomers. Upon hydrolysis the starch is converted into glucose units. The glucose upon oxidation produces carbon dioxide, oxygen, and energy. On the other hand, animals also store energy by linking many glucose molecules to form glycogen which is another form of starch. Carbohydrates also function as a support in plants. The cell wall of plant cells is made up of cellulose. Cellulose is another type of polysaccharides and is the major component of wood.
Carbohydrates have many applications including its use as a source of energy. Carbohydrates provide instant energy to the human body. Due to its high solubility in water glucose is readily soluble in water and instantly transported to the tissues through the bloodstream. Carbohydrates are used in making clothing. These carbohydrates include linen and cotton which are two forms of cellulose. They are also used in construction of buildings and houses in the form of wood. Other applications include combustion of wood to obtain heat and making paper.
Following figure depicts different compounds demonstrating the structural diversity of carbohydrates.