Other Important Sugars and their Derivatives
Other Important Sugars and their Derivatives
There are many different important compounds derived from carbohydrates. These derivatives of sugars resemble the structure of carbohydrates, but they are not simple ketoses or aldoses. Following are some important derivatives of carbohydrates discussed in detail.
Amino Sugars:
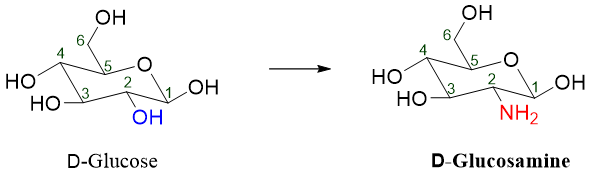
In amino sugars the -OH group at a non-anomeric carbon atom is replaced by an amino group. For example, if the -OH group present at the C2 position of D-glucose is replaced by -NH2 it forms D-glucosamine. D-glucosamine is the most common amino derivative of sugar found in nature. Glucosamine is available in different over-the-counter medicines to treat osteoarthritis.
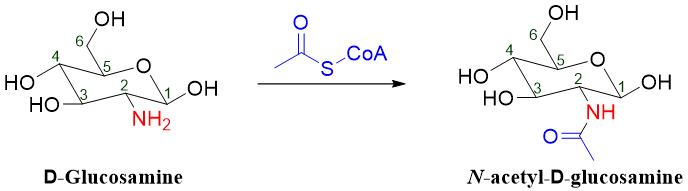
The acetylation of D-glucosamine with acetyl CoA produces N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (NAG).
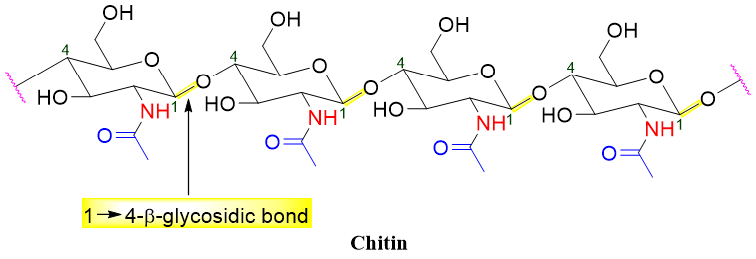
NAG upon polymerization (joined together by 1🡪4-β-glycosidic bonds) forms a polysaccharide called Chitin. Chitin forms the exoskeleton of many crustaceans and insects. The structure of chitin resembles the skeleton of cellulose except that the -OH present at C2 position in cellulose is replaced by -NHCOCH3 in chitin.
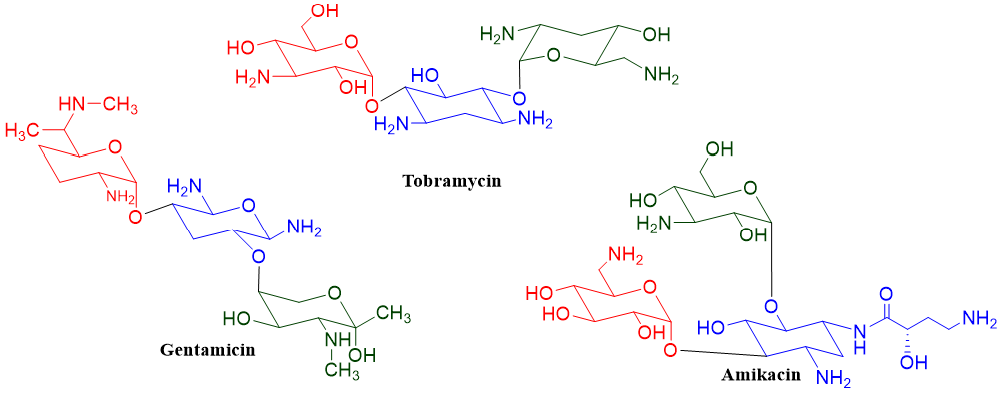
There are several amino sugar derivatives used for the treatment of many diseases for example, gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin are amino derivatives of trisaccharides used as potent antibacterial drugs.
N-Glycosides:
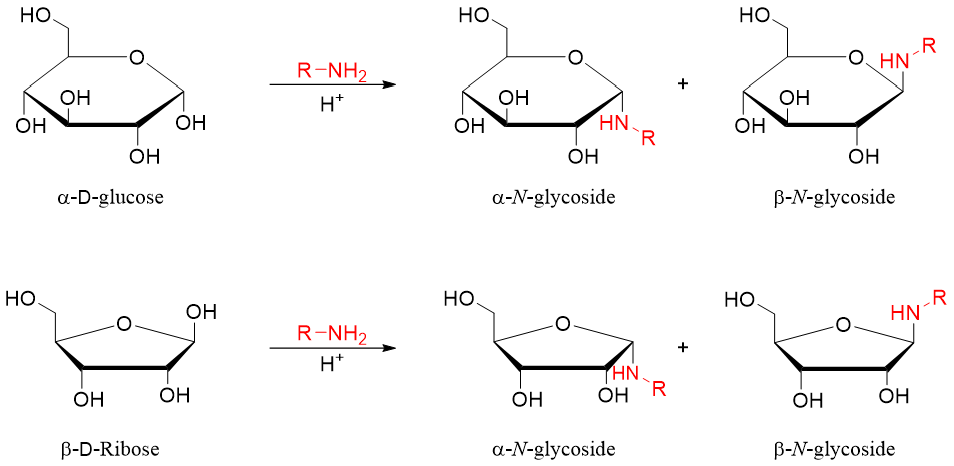
When monosaccharides are reacted with amines in the presence of mild acid N-glycosides are formed. This reaction results in the formation of two anomers as shown below.
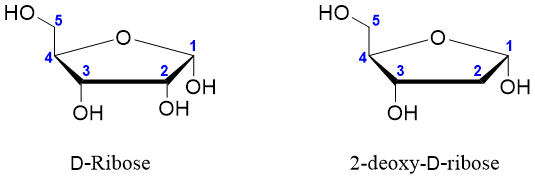
The N-glycosides formed by D-ribose and 2-deoxy-D-ribose sugars are of significant importance. These sugars form the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). Following are the structures of D-ribose and 2-deoxy-D-ribose (lacks -OH group at C2 position) sugars.
Following are the N-glycosides formed by D-ribose and 2-deoxy-D-ribose sugars linked to the nitrogenous bases via β-N-glycosidic bonds.
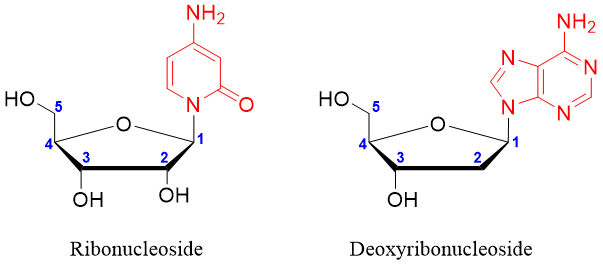
There are five distinct types of nitrogenous bases. Two of them are derived from purines while the remaining three are derived from pyrimidines.
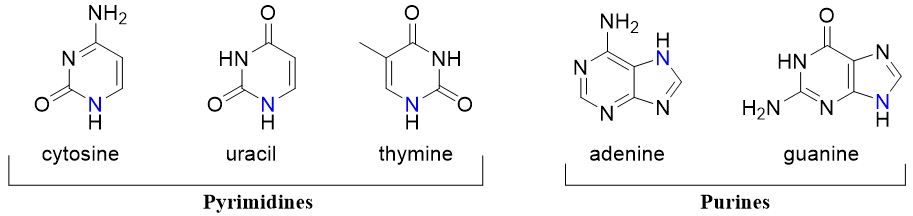
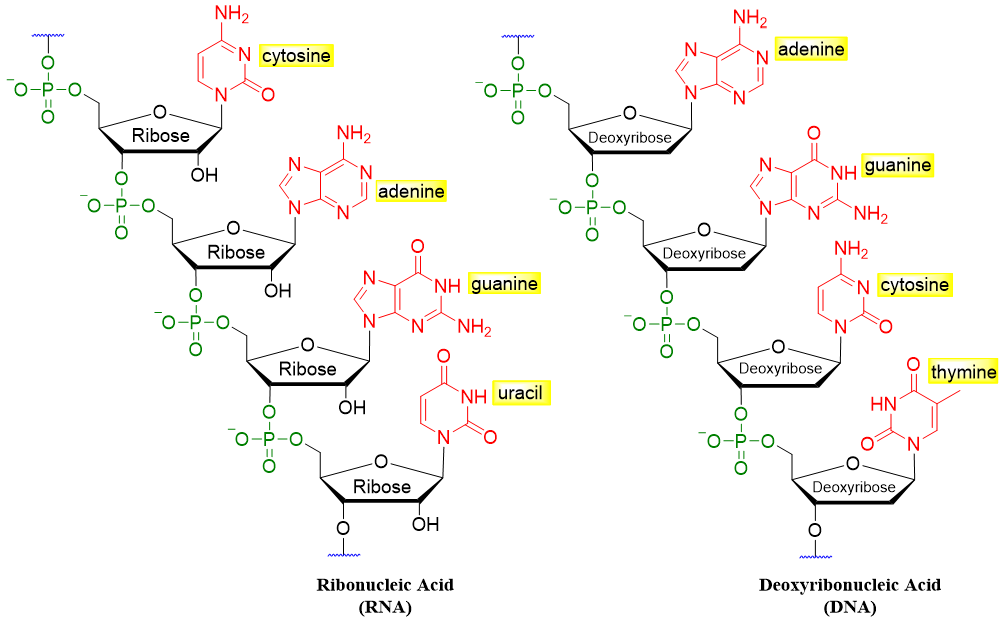
DNA is made up of deoxyribose sugar, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine whereas, RNA is made up of ribose sugar, adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine. The monomers of nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of nucleosides in which one of the -OH groups of sugar moiety is replaced by phosphate group.
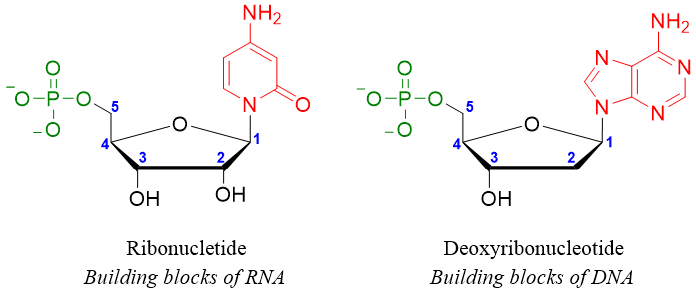
Following figure represents the short segments of DNA and RNA.