Disaccharides
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are sugars made up of two monosaccharides linked together by a glycosidic bond. The two linking monosaccharides can either be six-membered ring sugars or five-membered ring sugars. The two monomers are linked through an oxygen atom of an acetal group (C1) of one monosaccharide and C2 or C4 of another monosaccharide. The glycosidic linkage can either be alpha (α) or beta (β) as shown below.

Following are some most abundant disaccharides found in nature.
Sucrose:
Sucrose is the most common disaccharide found in table sugar and sugarcane. Sucrose is made up of two different monosaccharides, glucose (six-membered ring sugar) and fructose (five-membered ring sugar). In sucrose the α-glycosidic bond is formed between the anomeric carbon (C1) of glucose and anomeric carbon (C2) of fructose.

As shown above the sucrose molecule has two acetal groups (C1 of glucose and C2 of fructose) and there is no hemiacetal group present in it. This makes the sucrose molecule a non-reducing sugar and prevents it from undergoing mutarotation.
Maltose:
Maltose is the disaccharide found in grains. Maltose is made up of α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose units connected via 1🡪4-α-glycosidic linkage. In maltose the α-glycosidic bond is formed between the anomeric carbon (C1) of α-D-glucose and C4 carbon of β-D-glucose.

As shown above the maltose molecule has one acetal group (C1 of α-D-glucose) and one hemiacetal group (C1 of β-D-glucose). The presence of hemiacetal group makes the maltose molecule a reducing sugar and allows it to undergo mutarotation and makes it to exist both in alpha and beta anomeric forms.

Cellobiose:
Cellobiose is the disaccharide formed by the hydrolysis of cellulose polysaccharide. Like maltose, the cellobiose is also made up of two glucose units. The difference occurs between the type of glycosidic linkage formed between the two glucose units. Unlike maltose, in cellobiose both glucose units are β-anomers and they are connected via 1🡪4-β-glycosidic linkage as shown below.
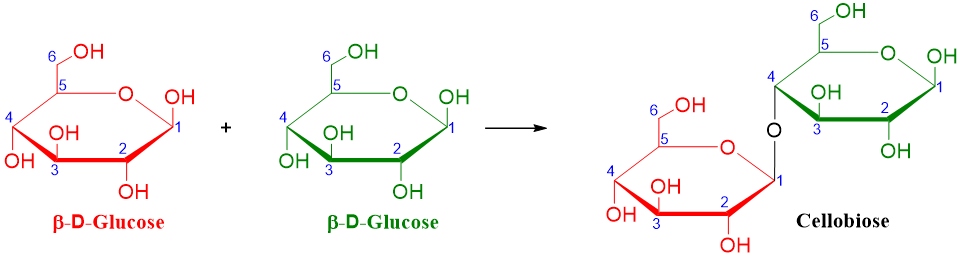
As shown above the cellobiose molecule has one acetal group (C1 of one glucose unit) and one hemiacetal group (C1 of other glucose unit). The presence of hemiacetal group makes the cellobiose molecule a reducing sugar and allows it to undergo mutarotation and makes it to exist both in alpha and beta anomeric forms.

Lactose:
Lactose is the disaccharide found in human and cows milk. Lactose is made up of one glucose and one galactose units connected via 1🡪4-β-glycosidic linkage. In lactose the β-glycosidic bond is formed between the anomeric carbon (C1) of galactose and C4 carbon of glucose.

As shown above the lactose molecule has one acetal group (C1 of galactose) and one hemiacetal group (C1 of glucose). The presence of hemiacetal group makes the lactose molecule a reducing sugar and allows it to undergo mutarotation and makes it to exist both in alpha and beta anomeric forms.

