Lengthening and Shortening of Sugar Chain
Lengthening and Shortening of Sugar Chain
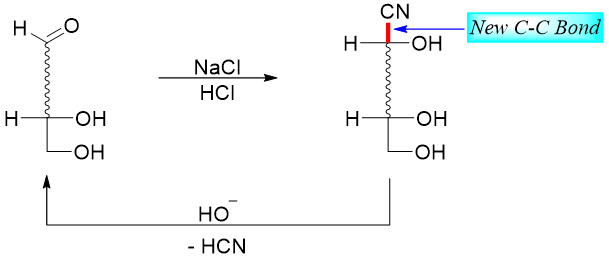
In carbohydrate chemistry, two common methods are used to add or remove one carbon atom from the aldose skeleton. The Kiliani-Fischer synthesis adds one carbon atom and results in an increase in the aldose chain whereas, Wohl degradation method removes one carbon atom and results in a decrease in the aldose chain. Both reactions involve cyanohydrin intermediates. Following scheme shows the lengthening (addition of HCN) and shortening (reaction with base) of a sugar chain.
Kiliani-Fischer Synthesis:
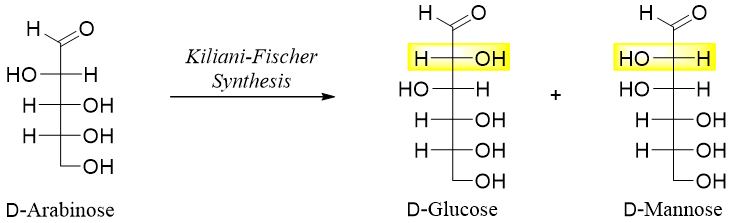
In this reaction a new chiral carbon is added at position C2. The product formed has two epimers with different configurations at C2 position. For example, the addition of one carbon at position C2 of D-arabinose will form two epimers, D-glucose and D-mannose.
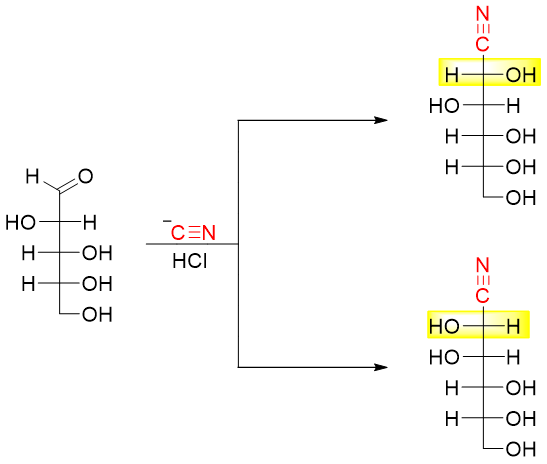
The above reaction consists of three steps. In the first step the HCN is added to the carbonyl group. The addition -CN to the carbonyl group generates two new stereocenters which will later form two epimers.
In the second step the nitrile (-CN) functional group is reduced to an imine using partially deactivated catalyst like Pd-BaSO4 (Lindlar catalyst) and hydrogen gas (H2) to avoid complete reduction of nitrile to an amine.
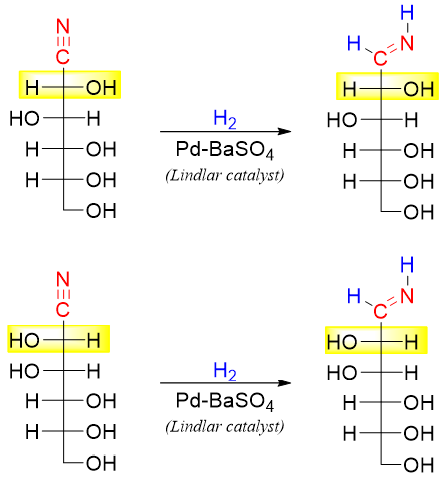
In the last step the imines are hydrolyzed to corresponding aldoses (epimers).
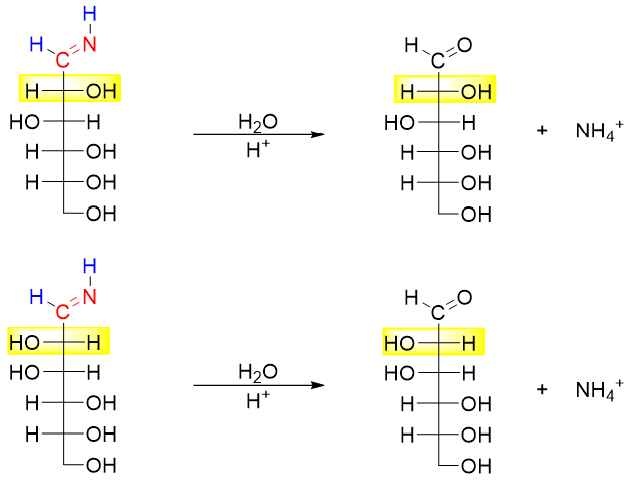
Wohl Degradation:
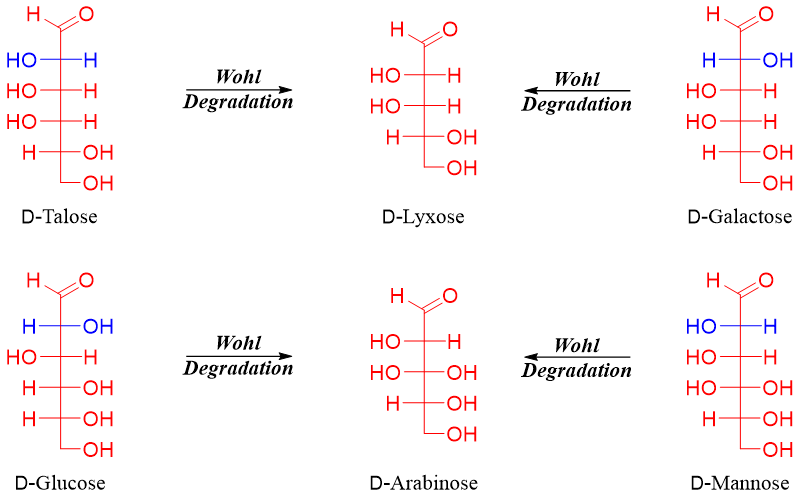
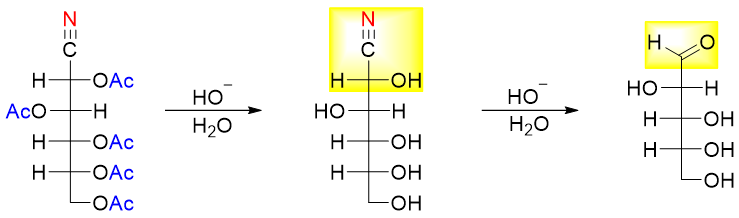
In this reaction one carbon atom is removed present at position C1. A single product is formed and the stereochemistry of chiral centers of the starting material are preserved. For example, the removal of carbon atom at position C1 of D-glucose will form a single product, D-arabinose.

The above reaction consists of three steps. In the first step the aldehyde group of D-glucose reacts with hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to form corresponding oxime.
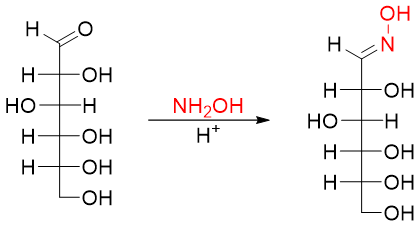
In the second step the oxime is heated with acetic anhydride. This results in dehydration of the oxime group into cyano group and converting other hydroxyl groups into esters.
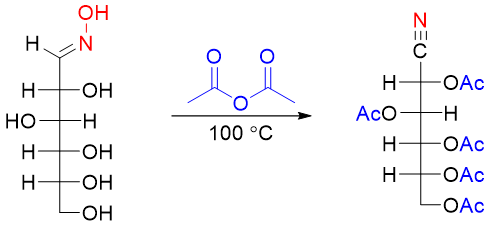
In the final base catalyzed hydrolysis of ester into hydroxyl groups and the conversion of cyano group into aldehyde is conducted.
Those sugars which are epimers of each other at position C2 upon Wohl degradation reaction produce the same product. For example, D-galactose and D-talose produce D-lyxose as a sole product while D-glucose and D-mannose produce D-arabinose as a single product.