Reactions of Amino Acids
Reactions of Amino acids
Amino acids having both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups can undergo the standard reactions of these groups. As both functional groups can interfere with each other therefore, the reaction conditions are carefully selected. Some of these reactions are discussed below.
Reactions of Amino Group:
The amino group of amino acids upon reaction with acylating agents forms an amide functional group. This reaction is conducted to protect the amino group and to stop it from undergoing unwanted nucleophilic reactions. Different acylating agents like acid anhydride and acid chlorides are used for the acylation of amide groups.
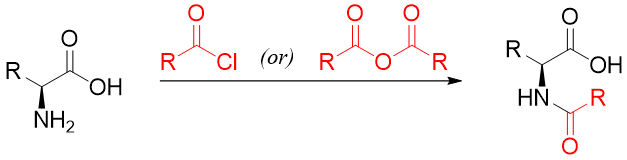
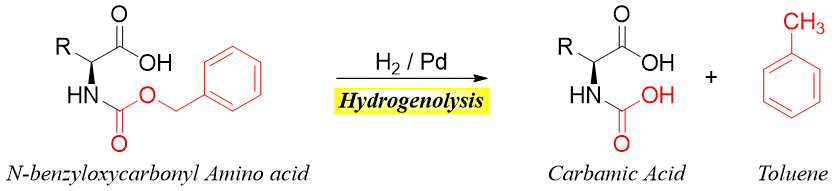
Two commonly used acylating agents are acetic anhydride and benzyl chloroformate. Benzyl chloroformate reacts with an amino group of amino acids to produce N-benzyloxy carbonyl derivative which is often formed in peptide synthesis to protect the amino group.
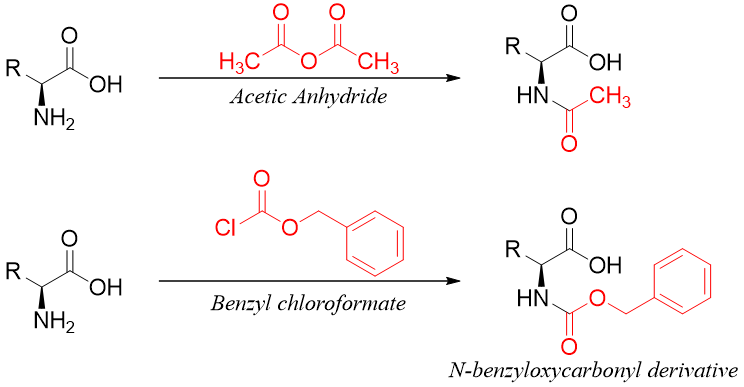
N-benzyloxy carbonyl derivative is a carbamate ester. The carbamate ester has an amide part and a benzyl ester part.
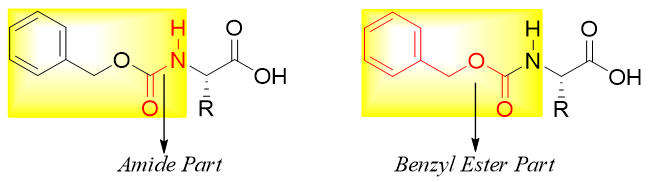
The amide part of carbamate ester is easily hydrolyzed while the benzyl ester part undergoes hydrogenolysis when treated with H2.
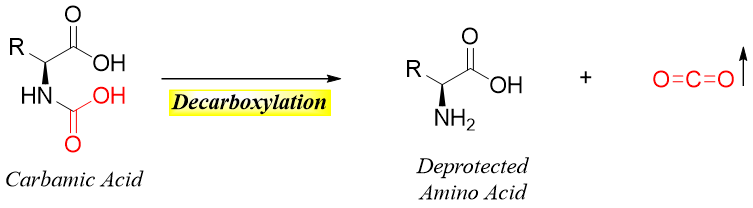
The carbamic acid formed by the catalytic hydrogenolysis of N-benzyloxy carbonyl amino acid is highly unstable hence, it undergoes a decarboxylation reaction to give deprotected corresponding amino acid.
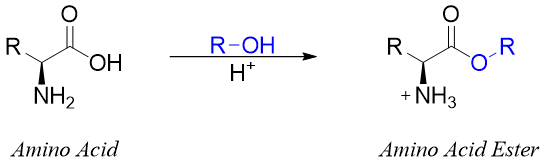
Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Group:
Amino acids upon reaction with alcohols in the presence of acid catalysts undergo esterification reactions. Since the reaction is conducted in acidic medium therefore, the amino group is protonated making it lose its nucleophilicity.
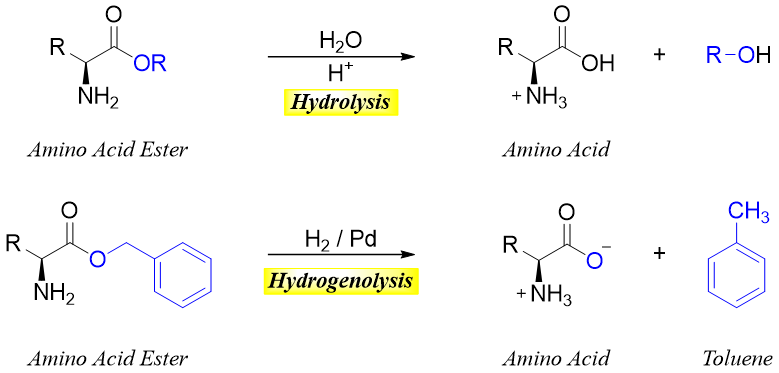
The esterification of the carboxylic group of amino acids is often conducted to protect it and to stop it from undergoing unwanted reactions. For this purpose, the methyl, ethyl, and benzyl esters are used to protect the carboxylic group. Benzyl esters can be removed by both acidic hydrolysis and hydrogenolysis.
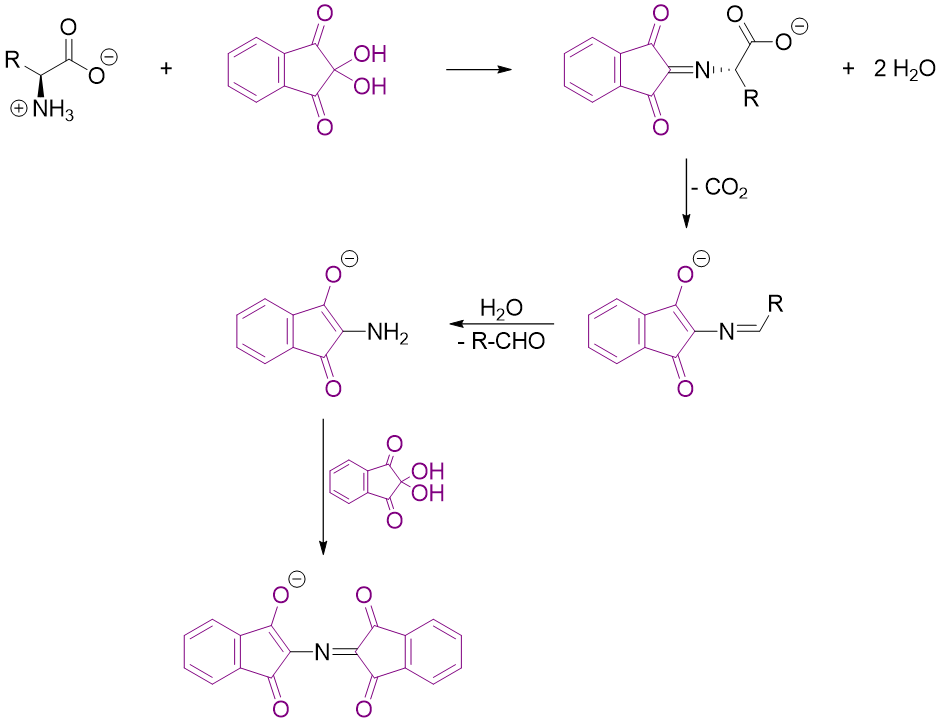
Reaction of Amino acids with Ninhydrin:
Ninhydrin is a common reagent used in bioanalytical techniques for the analysis of amino acids. When ninhydrin is reacted with primary amino acids (containing -NH2 groups) it produces Ruhemann's purple. Ruhemann's purple is a resonance stabilized anion and has deep violet color. During this reaction, the remaining part of the amino acid is converted into carbon dioxide gas and aldehyde.
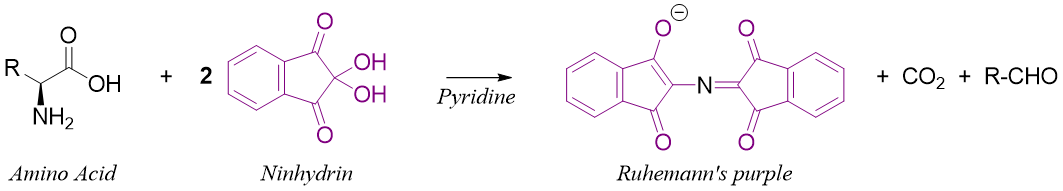
This reaction is used to detect amino acids on a variety of substrates. This test can be used to detect and visualize fingerprints. The human fingers upon touching any surface leaves a trace amount of amino acids which are present in human secretions. When this surface is treated with ninhydrin and pyridine it forms a purple color and makes visible the fingerprints. Following scheme shows the steps involved in the synthesis of Ruhemann's purple.