Peptides
Peptides
When two or more amino acids are joined together via a peptide bond (an amide bond), they form peptides and proteins. If the peptide is made up of two amino acids (single amide bond) it is called dipeptide, if there are three amino acids (two amide bonds) it is called tripeptide. In polypeptides (proteins) the number of amino acids can range from tens to thousands.
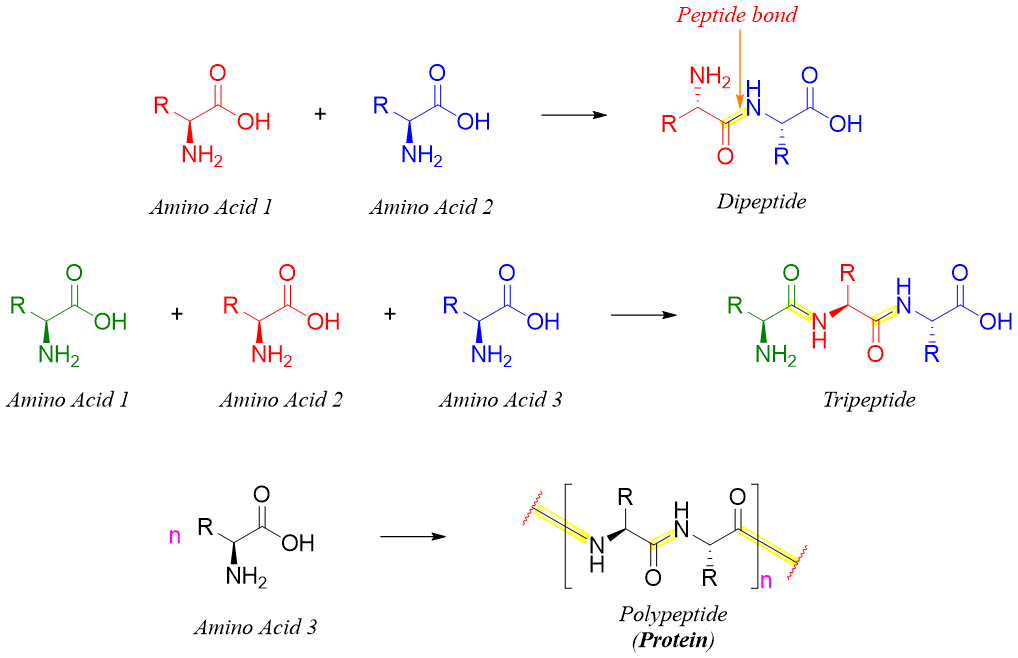
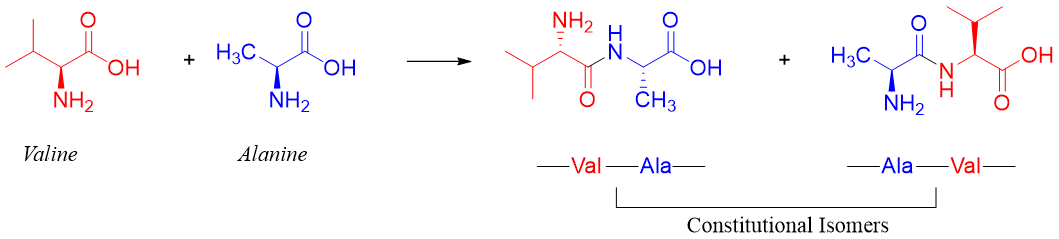
By convention, the C-terminal of peptides is always written on the right hand side of the chain and the N-terminal is written on the left hand side of the peptide chain. Since each amino acid contains both amino and carboxylic acid groups therefore, when two amino acids are reacted, they can form two different dipeptides and when three amino acids are reacted, they can form six different dipeptides. Remember we are ignoring the self-reaction of amino acids. For example, valine and alanine give two different dipeptides. These two different dipeptides are constitutional isomers of each other.
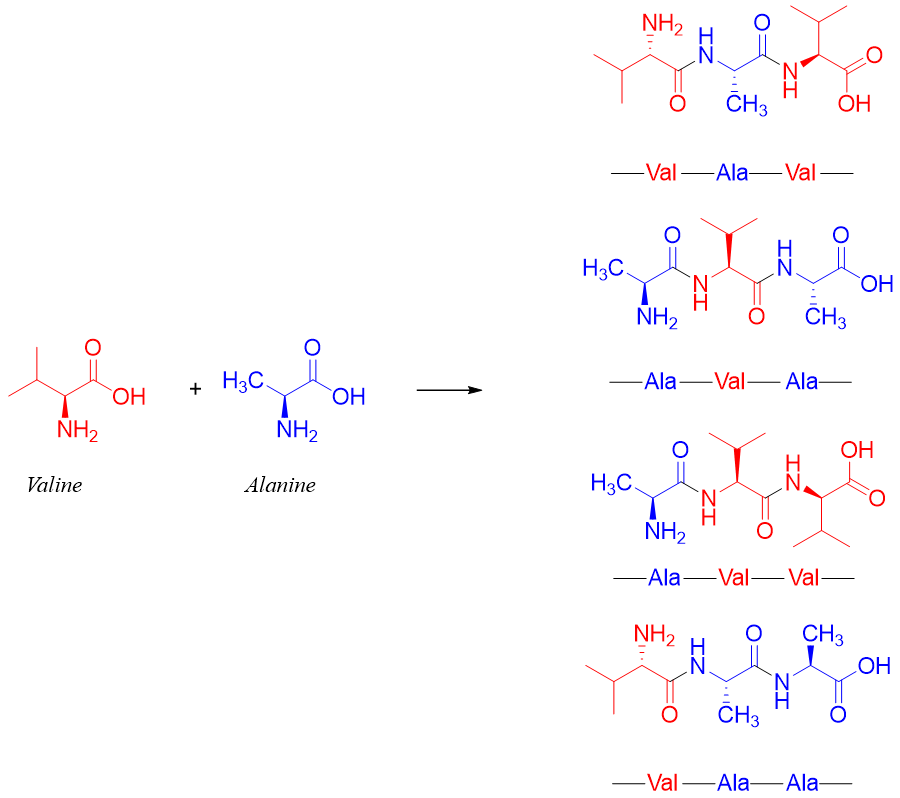
Similarly, a single amino acid can form one tripeptide, two amino acids can form two tripeptides, and three amino acids can form six tripeptides. For example, valine and alanine will form following four tripeptides.
Peptides are named by the names of amino acids making the peptides. The name starts from the N-terminus and ends at the C-terminus. In a more convenient shorthand method, each amino acid is either represented by a three letter abbreviation or a single letter symbol sequenced and arranged from N-terminus to C-terminus. For example, in chignolin there are ten amino acids.
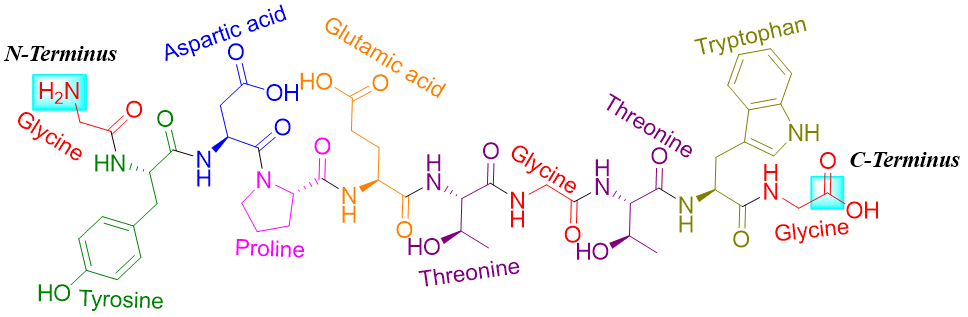
The sequence starts at N-terminus (glycine) and ends at C-terminus (glycine). The three letter abbreviation and a single letter symbol name of this polypeptide is as follows.

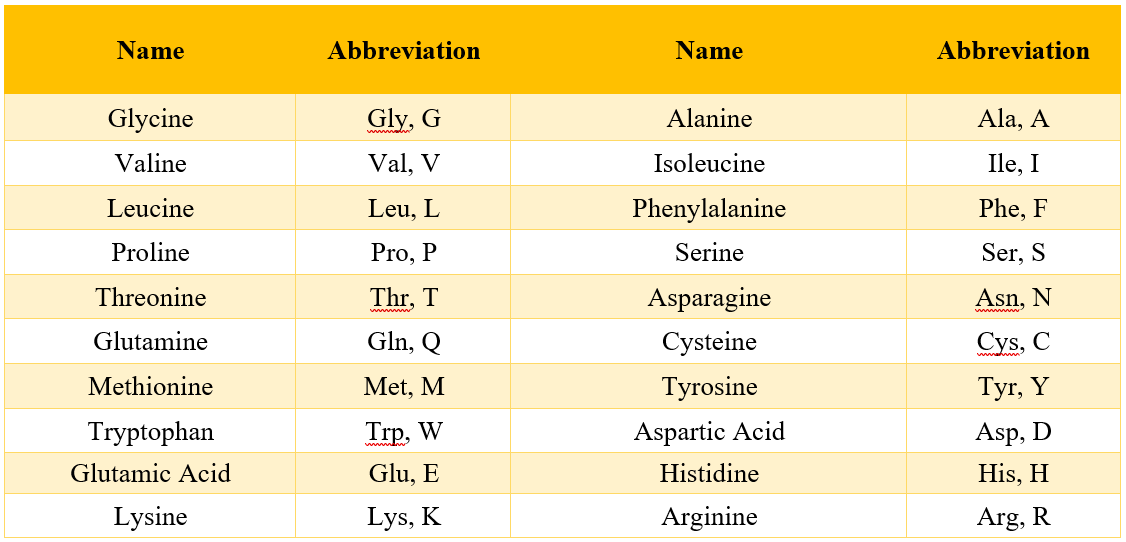
Following table shows the three letter abbreviations and single symbols of standard amino acids.
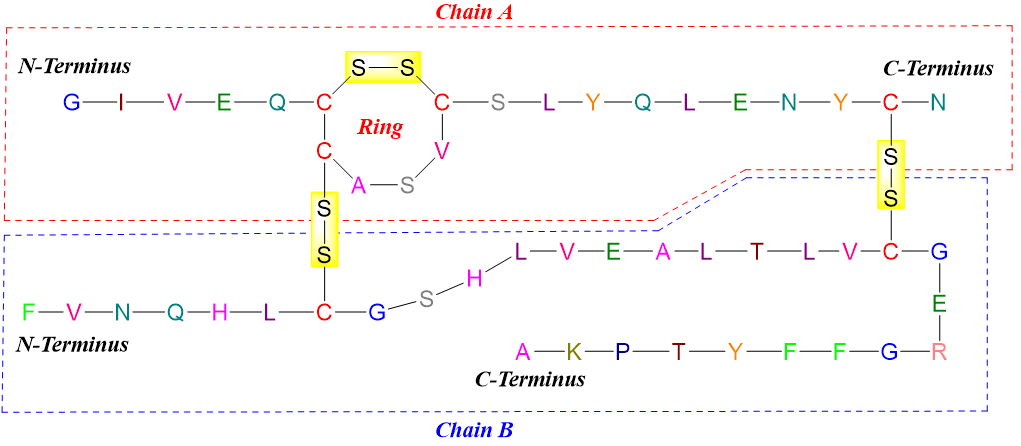
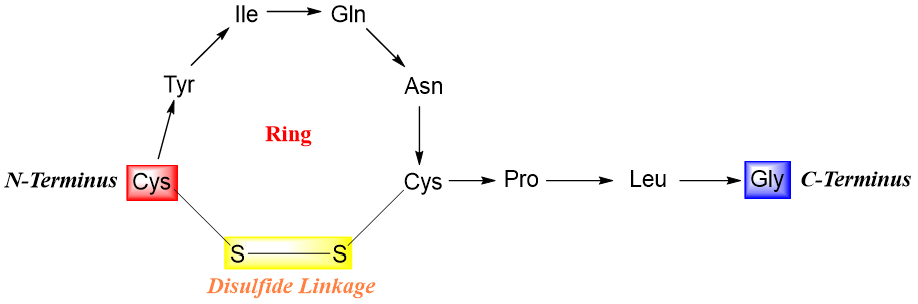
Those peptides which contain cysteine residues can also have different covalent bonds other than peptide bonds. These bonds are called disulfide linkages also known as disulfide bridges. Disulfide bonds can either form between two chains or it can link a single chain into a ring(s).
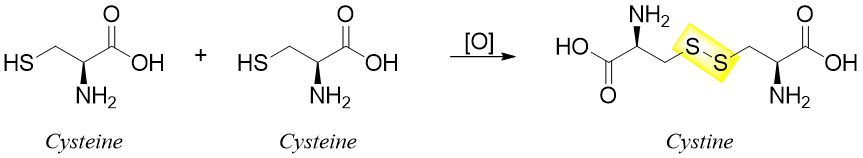
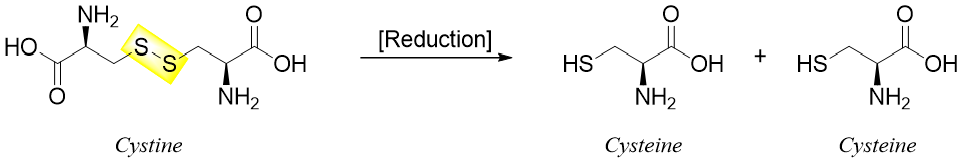
The formation of disulfide bonds is an oxidation reaction and can take place in mild oxidizing conditions. Similarly, a mild reduction can cleave the disulfide bond.
Following figure shows the formation of disulfide bridge between the cysteine residues of the same peptide chain in human oxytocin forming a ring.
Following figure shows the structure of bovine insulin. In this structure there are three disulfide linkages. Two disulfide bonds are linking the two peptide chains while one is forming a ring in chain A.