Introduction
Introduction
Proteins are the most abundant biopolymers contained by animals. Proteins play particularly important roles in controlling functions and structures of human body. Protein is a very key component part of our daily life diet as it helps in making new and repairing old cells hence, involved in direct growth. Proteins are long chains of α-amino acids linked together via peptide bonds. In α-amino acid an amino group is bonded at alpha position of a carbonyl group (carboxylic acid). The overall chemical and physical properties of a protein depend on the types of amino acids it is made up of. The general structure of an α-amino acid is shown below.
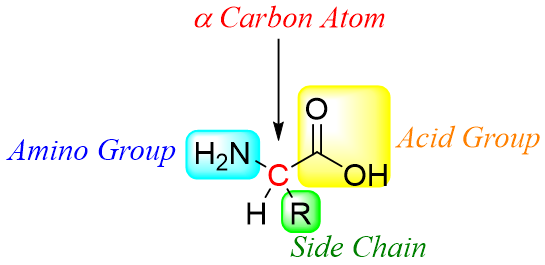
There are about twenty naturally occurring amino acids. Each amino acid has different side chain bonded to alpha carbon. In proteins the amino acids are joined together via a peptide bond. The peptide bond is formed between the α-amino group of one amino acid and carbonyl group of another amino acid. The peptide bond is usually an amide bond. Following scheme depicts the formation of a peptide bond.
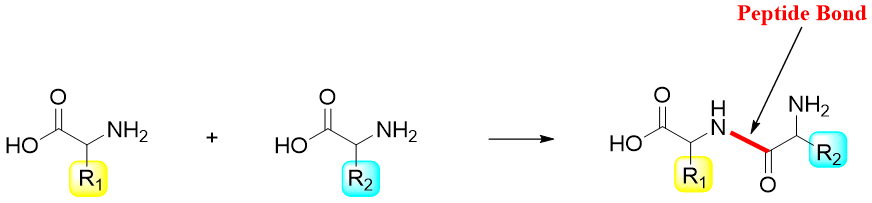
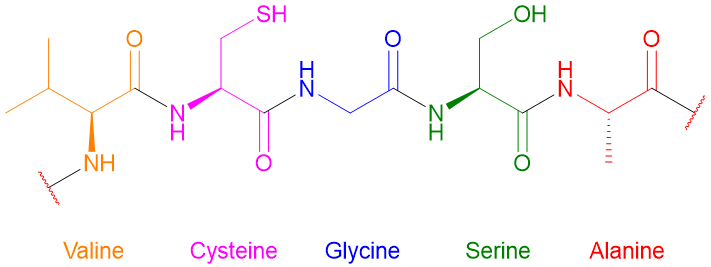
Those peptides which are made up of two amino acids are called dipeptides, in tripeptide there are three amino acids, whereas, in oligopeptides the number of amino acids is four to ten. Polypeptides contain more than ten amino acids. In proteins the number of amino acids can vary from 20 (TRP-cage) to 27000 (Titin). Following figure depicts the structure of general protein.
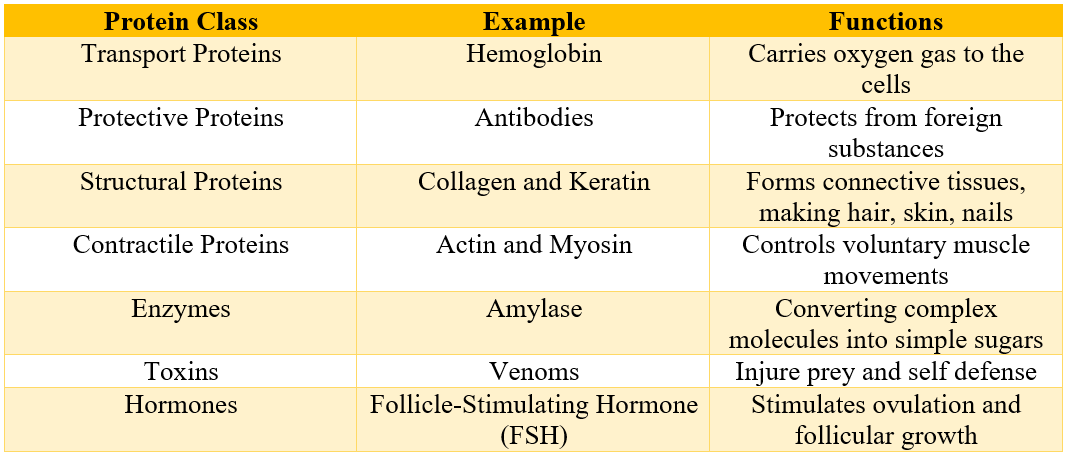
The types and sequence of amino acids present in a protein has a range of structural and catalytic properties. Due to this proteins are found to be involved in controlling variety of functions in an animal body. Following table shows some principal functions carried out by different classes of proteins.
The proteins are further classified as globular or fibrous. In globular proteins have spherical shape and are insoluble in water. Most of the enzymes are globular proteins. In fibrous proteins the amino acids are linked in a thread like structure, and they are insoluble in water. All structural proteins are fibrous proteins.
