Malonic Ester Synthesis
Malonic Ester Synthesis
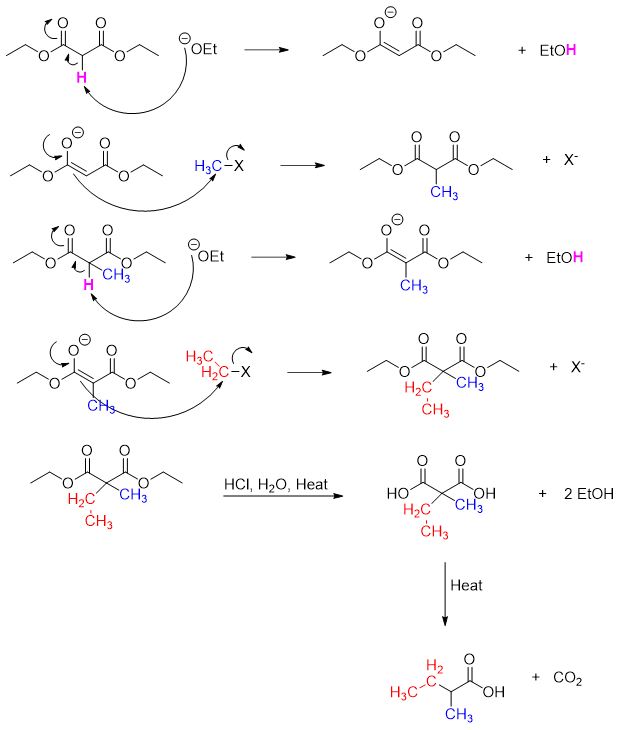
The synthesis of carboxylic acids with desired chain length via alkylation of malonic ester followed by decarboxylation reaction is called as malonic ester synthesis.
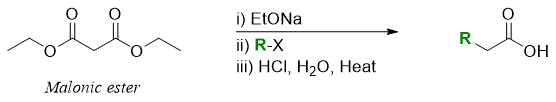
Mechanism:
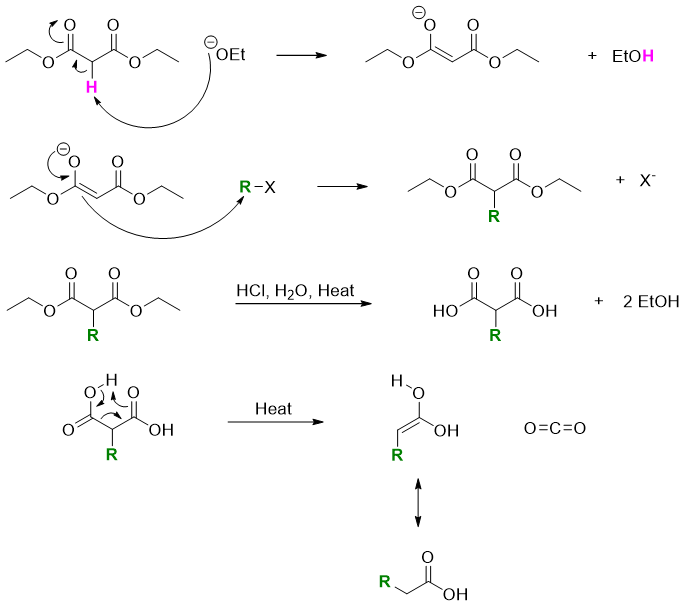
In the final product the alpha carbon and carboxylic group come from malonic ester. Any other substituent at the alpha position comes from the alkyl halide.
Retrosynthetic analysis:
The malonic ester synthesis can be used to prepare any desired carboxylic acid. For example, for the synthesis of 2-methylbutanoic acid following procedure is adopted.
First identify the groups coming from melonic ester and alkyl halide(s).
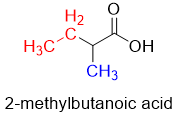
There are two substituents (red and blue) at alpha position. These two substituents will come from alkyl halides. Next, the alpha carbon and carboxylic group will come from malonic ester.
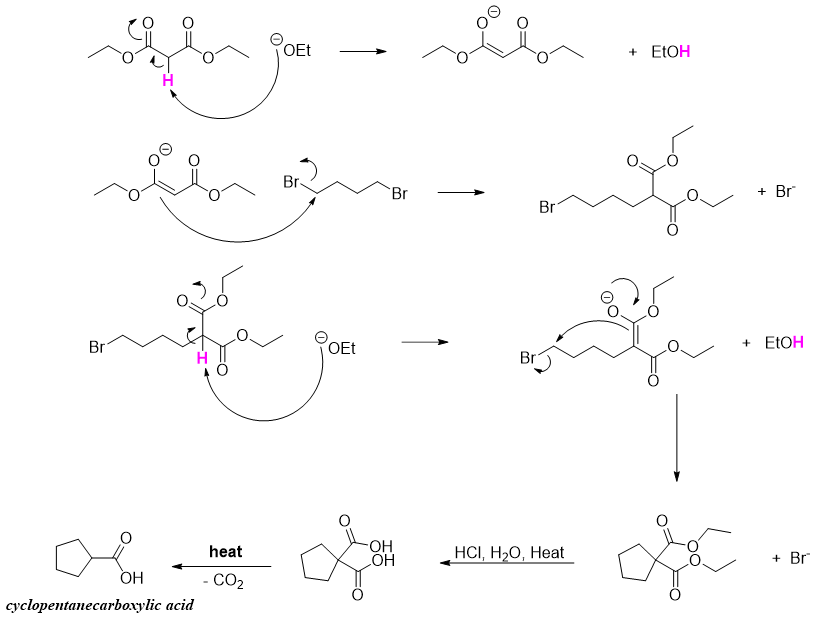
The malonic ester synthesis procedure is also utilized to prepare cycloalkane carboxylic acids. For example, when melonic ester is reacted with 1,4-dibromobutane in the presence of two equivalents of base followed by decarboxylation forms cyclopentane carboxylic acid.