Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones
SYNTHESIS OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
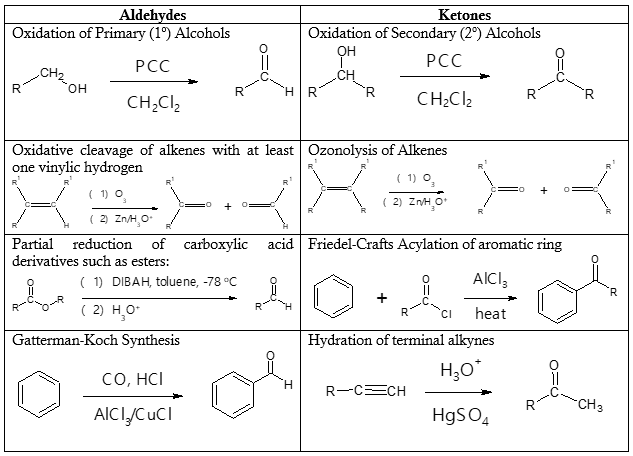
There are various methods or reactions wherein aldehydes and ketones can be prepared depending on the starting material. An overview of the reactions leading to aldehydes and ketones is illustrated in Table 1. We will look into each of the commonly used reaction pathways in this article.
Preparation of Aldehydes
- (1) Oxidation of Primary (1o) Alcohols
Primary alcohols can be partially oxidized to form aldehydes. This means that careful selection of oxidizing agent must be employed to avoid over-oxidation to carboxylic acid. Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), a complex of chromium trioxide with pyridine and HCl, in dichloromethane (DCM) solvent at room temperature is commonly used for this purpose. Specific example is shown below.
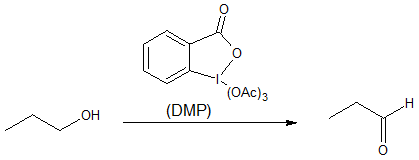
Other possible route that also converts primary alcohols to aldehydes without using hazardous chromium compounds is either Swern oxidation or Dess-Martin periodinane (DMP). Swern method uses dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as oxidant while Dess-Martin utilizes a high-valence iodine compound as the oxidant.
Swern oxidation:

Dess-Martin periodinane reaction:
- (2) Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes with vinylic hydrogen
Alkenes with at least one vinylic hydrogen (hydrogen atom attached to a C=C) can undergo oxidative cleavage when treated with ozone producing aldehydes.
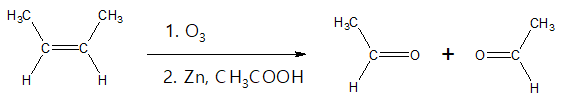
Notice that in the above example, each carbon of the C=C has a hydrogen atom, so upon oxidative cleavage, it results to the formation of the aldehyde compounds. In the above case, the aldehyde products are the same but they could also be different depending on the starting alkene.
- (3) Partial reduction of Carboxylic acid Derivatives
Certain carboxylic acid derivatives can also be partially reduced to form aldehydes. An example would be the reduction of an ester using diidobutylammonium hydride (DIBAH) which is normally carried out at -78 oC (dry-ice temperature) in toluene solution.
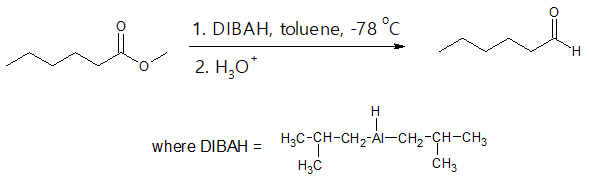
- (4) Gatterman-Koch Synthesis
Another variant of Friedel-Crafts acylation which yields aldehyde compound is the Gatterman-Koch formylation. It is called as such since the carbon monoxide (CO) and HCl used in the reaction generate an intermediate that reacts in the same manner as formyl chloride. The only limitation of this method is that only benzene and activated benzene derivatives can be used as starting material.
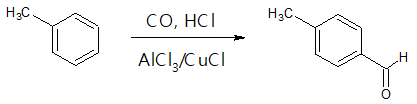
Preparation of Ketones
For most part, notice the similarity of the methods for the synthesis of ketones with that of aldehydes.
- (1) Oxidation of Secondary (2o) Alcohols
Ketone formation from secondary alcohols is somewhat a flexible reaction to conduct since both mild and strong oxidizing agents can be used. The choice of oxidant just depends on the desired yield, cost and sensitivity of the starting alcohol with acid or base. You don’t have to worry about overoxidation of the alcohol to a carboxylic acid anymore. Some examples are shown below.
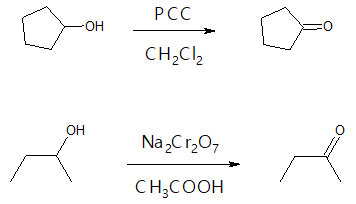
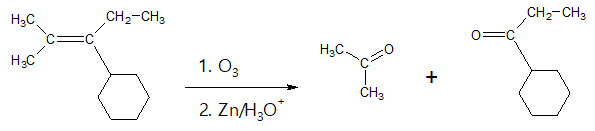
- (2) Ozonolysis of Alkenes
If one or both of the unsaturated carbons (carbon involved in the C=C) is disubstituted or simply put it as a tetrasubstituted alkene, then carrying out ozonolysis will yield the corresponding ketone compounds. As a review, ozone is perhaps the most useful double-bond cleavage reagent.
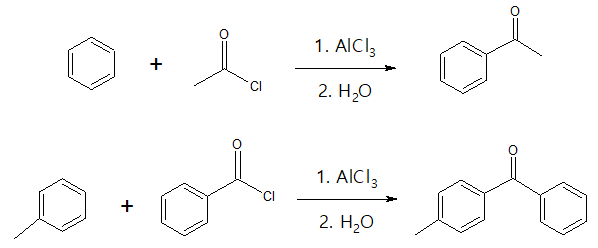
- (3) Friedel-Crafts Acylation of Aromatic Ring
If one wants to synthesize aryl ketones or diaryl ketones, then Friedel-Crafts acylation would be the best option. Just take note that this particular reaction will not work when the aromatic ring is bonded to electron-withdrawing group which will deactivate the benzene ring, reducing its reactivity.

- (4) Hydration of Terminal Alkynes
This method is ideal if one wants to synthesize methyl ketones. Hydration of alkynes can be catalysed by combination of sulphuric acid and mercuric ion. The initial enol formed from Markovnikov hydration of the alkyne will favourably tautomerize to the keto form.
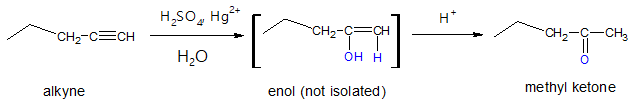
Internal alkynes can still be hydrated but the disadvantage would be the mixture of ketone products that are formed. The utilization of terminal alkynes is more specific, yielding only one ketone compound.
