Alpha Reactions
Alpha Reactions
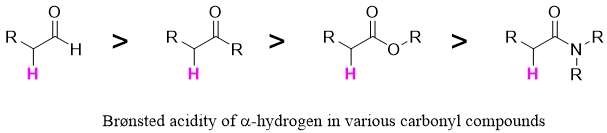
The carbon acidity of amides is weaker than aldehydes, ketones, and esters. This is due to high π-donor ability of the nitrogen atom which makes the amide highly stable. The α-alkylation reactions of amides are challenging due to their lower Brønsted acidity of α-hydrogen.
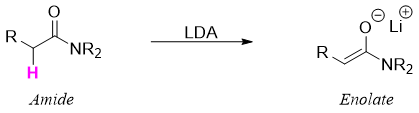
Amides containing alpha hydrogens can be converted into enolates by treating it with lithium diisopropylamide (LDA).
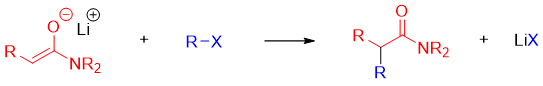
The amide enolate formed can further reacted with different electrophiles to form new C-C bonds.
For example,
The Claisen condensation reaction between amides and esters is often used to synthesize β-keto amides which serves as a useful building block in biologically active molecules.

However, the reaction between amide and ester requires harsh conditions such as using strong bases and very low temperatures as the alpha hydrogens of amides are very less acidic than aldehydes, ketones, and esters. This decrease in reactivity makes poor functional group compatibility of amides.
Due to less acidity of alpha hydrogens of amides, different approaches are adopted to make new C-C bonds at alpha position of amides. The α-carbon of an amide was activated by Hartwig under mild conditions using palladium catalysts. This method showed excellent functional group tolerance.

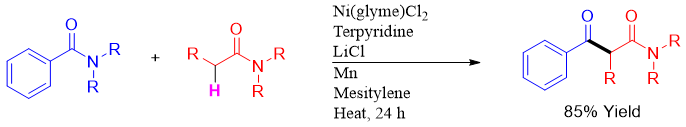
In another method, Claisen condensation reaction between two amides is developed to form β-keto amides. The reaction is Nickle and terpyridine catalyzed in the presence of LiCl and Mn. One amide possesses an alpha hydrogen.
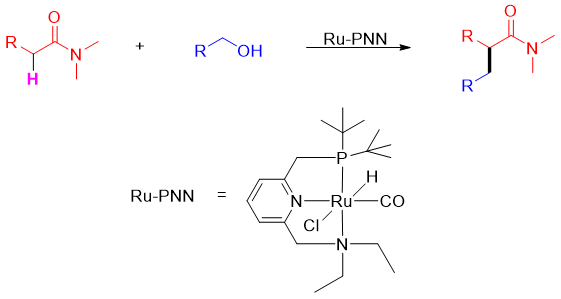
Alpha alkylation of amides can also be done by reacting amides containing alpha hydrogen with alcohols in the presence of Ru-PNN catalyst with turn over number upto 560.