Side chain Halogenation
Side chain Halogenation
Side-chain halogenation of alkylbenzene refers to the halogenation of alkylbenzene at benzylic position containing benzylic proton.
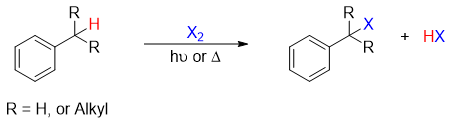
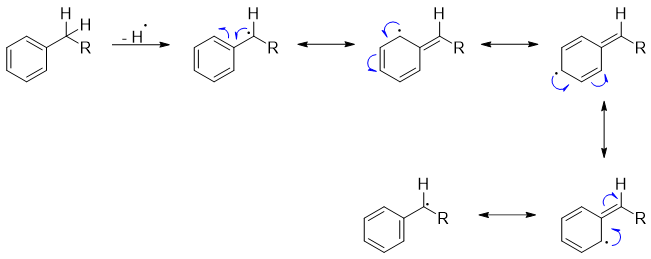
The benzylic carbon and hydrogen (C-H) bond is said to be the weakest sp3 hybridized bonds. This is since homolytic cleavage of C-H produces benzyl radical which is stabilized by resonance.
The side chain chlorination and bromination take place by reacting alkylbenzene with Cl2 and Br2 in the presence of light or heat. Bromination reaction can also be done using N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) in the presence of peroxide or light.
The mechanism of each reaction comprises of three steps.
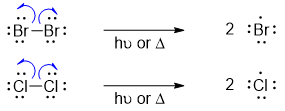
i) InitiationIn this step the bond between Cl2 or Br2 cleaves homolytically in the presence of heat or light to produce free radicals.
In this step the radical formed in first step abstracts the benzylic proton forming resonance stabilized benzylic radical. The benzylic radical further reacts with Cl2 or Br2 to form halogenated product along with another halogen radical which repeats the process again.
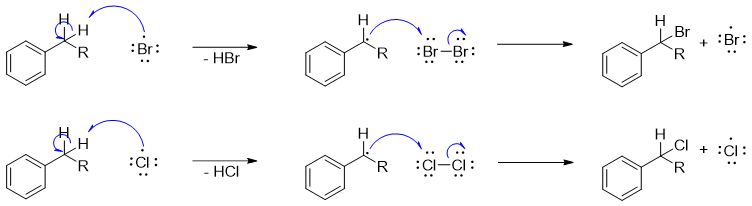
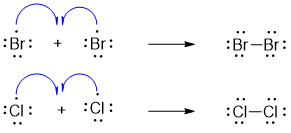
iii) Termination
The final step involves termination of reaction. In this step two radical species react with each other to form a single stable bond.
Bromination of alkylbenzene using N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) also called the Wohl-Ziegler bromination proceeds via a free radical mechanism.
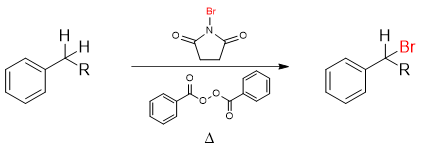
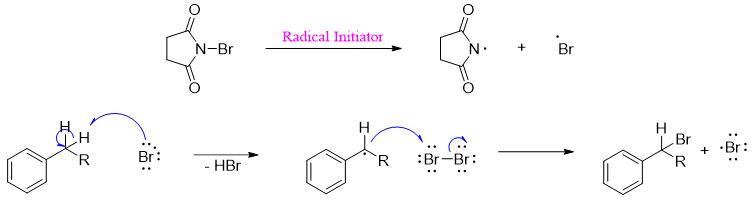
The Br2 molecule formed in situ is the main source of bromine radical.

Hence, alkylbenzenes containing benzylic proton(s) reacts in two different ways when treated with Cl2 and Br2 depending upon the conditions applied. If the reaction is performed using Lewis acid (FeCl3 or FeBr3) electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions take place, if light, heat, or any other radical initiator is used then side chain halogenation reactions take place.
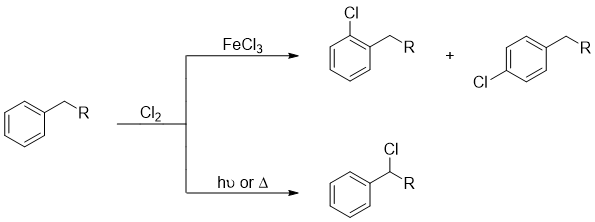
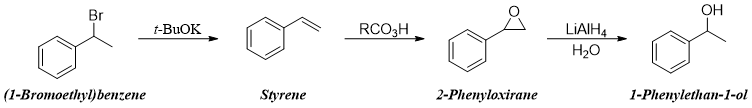
Side chain halogenation reactions of alkylbenzenes has many synthetical applications. The halogenated products can undergo nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions to produce many important compounds. Following examples shows some reactions involving halogenated compounds in synthesizing different functional groups.