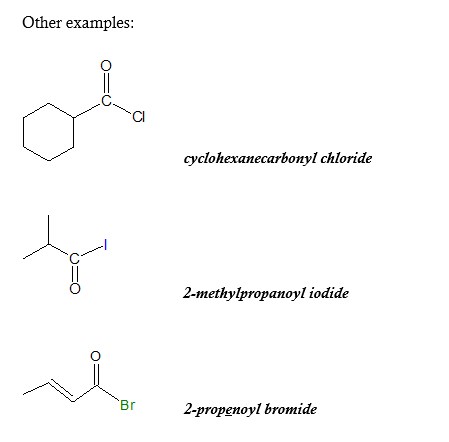
Nomenclature of Acyl Halides
Nomenclature of Acyl Halides
An acyl halide also known as an acid halide is derived from carboxylic acids by replacing a hydroxyl (-OH) group with a halide group. Carboxylic acid derivatives such as acyl halides are among the most widespread of all molecules, both in laboratory chemistry and in biological pathways. Thus, a study of them is fundamental to understanding organic chemistry

We can start learning more about acyl chlorides by looking at how these carboxylic derivatives are named. The nomenclature of acyl chlorides according to IUPAC rules are as follows:
- Identify the acyl group and the halide.
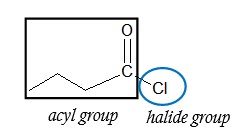
- Find the longest continuous carbon chain in the acyl group. Count the number of carbons and use the appropriate prefix representing the parent chain.
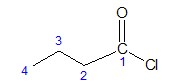
In our example, the acyl group contains four (4) C atoms. Thus, the prefix but- is used. Since acyl halides are derivatives of carboxylic acids, it would be ideal to give first the name of the corresponding carboxylic acid. Recall that in naming carboxylic acids the –e ending of the alkane corresponding to the parent chain is changed to –oic acid. When the –COCl group is bonded to a ring, the -carboxylic acid ending is changed to -carbonyl. Hence, the carboxylic acid name in our example is:
butane -----> butanoic acid
- For the acyl group, the name is derived from the carboxylic acid name by replacing –ic acid ending with –yl.
butanoic acid -----> butanoyl
- Lastly, add the name of the halide present in given structure. Use chloride for Cl, bromide for Br and iodide for I. In the example, Cl is present so the complete name would be:
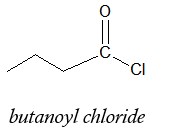
Applying the same rules to the next example, we obtain the name below: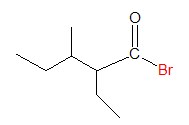
It is easy to identify the acyl group and halide group. Let’s move directly to the identifying the parent chain and figuring out the name of corresponding carboxylic acid.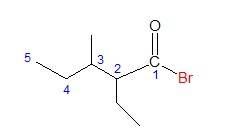
The longest continuous carbon chain in this case has five C atoms, so the name of the carboxylic acid would be pentanoic acid. Accordingly, the name of the acyl group is pentanoyl.
The other carbon groups are considered as substituents.
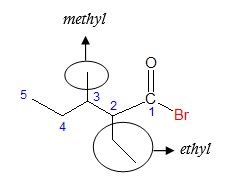
The parent chain has an ethyl group at C2 and a methyl group at C3. Integrating all the groups to complete the name, we have:
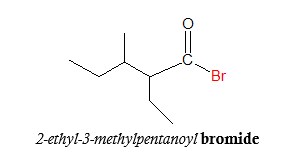
Note that the substituents should be mentioned alphabetically, just like in naming hydrocarbons.