Synthesis of Dienes
Synthesis of Dienes
The organic compounds having two C-C double bonds in them are called as dienes or Alkadienes.
Types of Dienes:
There are three types of dienes depending on the proximity of pi-bonds.
- Conjugated Diene
- Isolated Diene
- Cumulated Diene
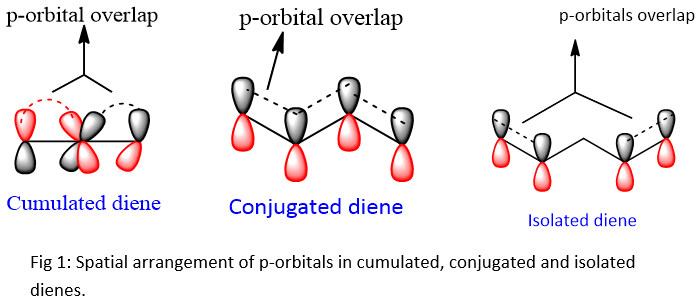
Conjugated Dienes: The dienes having alternative double and single bonds are called as conjugated dienes. Two π bonds are separated by single sigma bond.
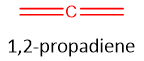
Cumulated Diene: These are a class of non-conjugated dienes in which the adjacent carbons are double bonded. These are also called as Allenes. Two π bonds are adjacent to each other.
Stability of Dienes:
From the dienes stated above, conjugated dienes are more stable as they are stabilized by resonance due to presence of delocalized pi-bonds in them. This delocalization results in decrease of energy of the system and as a result system become stable. The resonance stabilization in conjugated systems is shown below.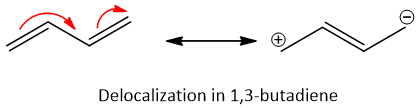
The arrangement of p-orbitals in all the dienes is shown below;
Synthesis of Dienes:
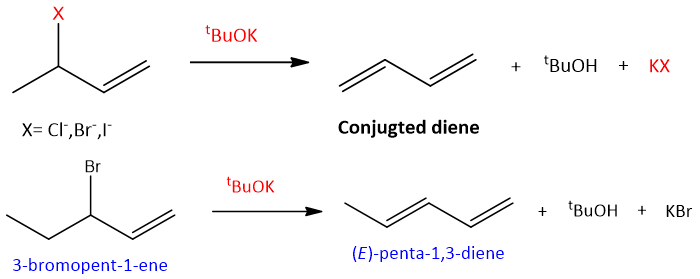
- Elimination reaction of allylic halides:
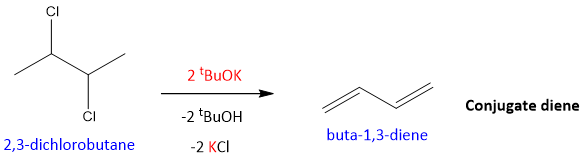
- Elimination reaction of vicinal dihalides:
This reaction is a double elimination reaction. A bulkier base is used to capture the proton which results in the formation of double bond simultaneously by the removal of halide ion. This results in the formation of conjugate diene.
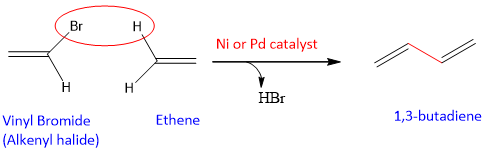
- The Heck Reaction:
It is a metal catalyzed coupling reaction of alkenyl halide (R-CH=CH-X) with an alkene. This coupling reaction results in the formation of new C-C bond between alkenyl halide and alkene by the release of hydrogen halide and end product is a conjugate diene. The catalysts used are soluble complexes of Ni and Pd.
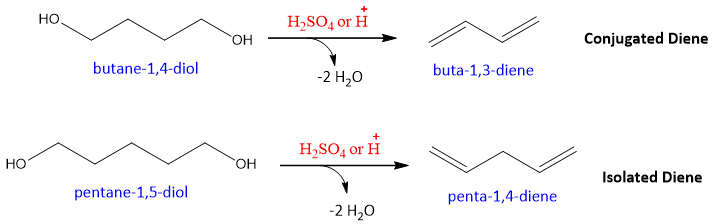
- Dehydration of diols:
Conjugated dienes can be prepared by the elimination reaction of diols (alcohols having two OH groups). This dehydration reaction takes place in the presence of acids.
- Pd catalyzed coupling reactions:
Pd catalyzed coupling reactions can synthesize all three types of dienes.
- 1. Stille Coupling: this is a coupling reaction of organo tin compounds with alkyl halides which results in the formation of C-C bond. The reaction is catalyzed by Pd metal. If both reactants have double bond in them (alkenyl halide and alkenyl tin), then their coupling will results in the formation of Conjugated diene. For example;
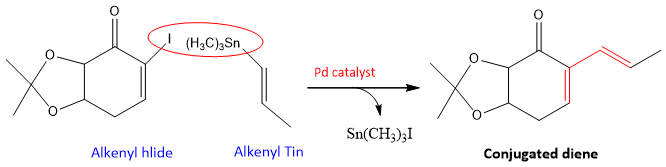
Sometimes, other compounds are also added to the reaction mixture that increases the efficiency of Pd catalyst. In this case CuI and arsenic derived ligands (AsR3) are used to increase the efficiency of this reaction.
If the reactants are Allylic halide and alkenyl tin compound then isolated dienes are formed as a result of this coupling.
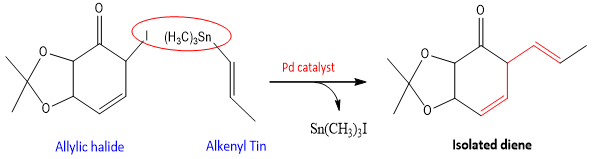
- 2. When an alkyne couple with organo Zn compound in the presence of Pd catalyst allenes are formed.
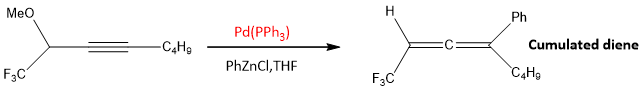
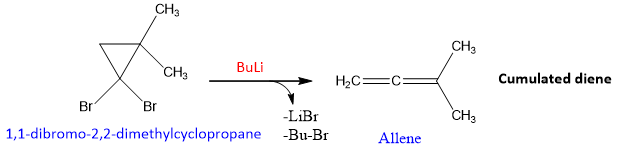
- Skattebol Rearrangement:
It is the reaction of converting geminal dihalo cyclo-propane into allene by using a organo-lithium compound as a base. It is a simple rearrangement reaction takes place as shown below;