Polymerization of Dienes
Diene Polymerization:
Introduction:
Dienes on treatment with strong acid undergo polymerization. Dienes polymerization has significant importance because it produce polymers having unreacted double bonds. Dienes can be polymerized in two ways
- 1,2-polymerization
- 1,4-polymerization
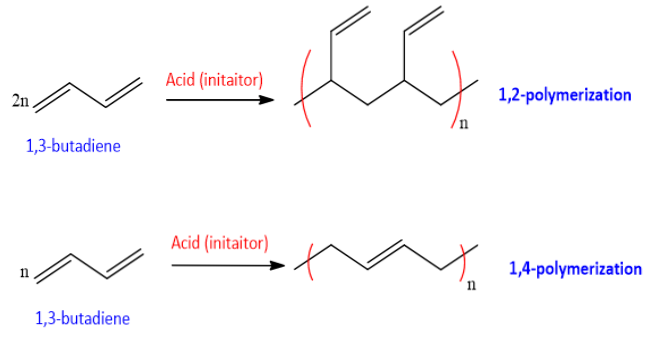
1,3-Butadiene on 1,2-polymerization gives polyethylene and on 1,4-polymerization polymerized to trans- polybutadiene, Cis-polybutadiene or mixed polymers.
Methods of diene polymerization
- Acyclic diene metathesis(ADMET)
- Ziegler-Natta polymerization
Acyclic diene metathesis(ADMET)
Terminal dienes can easily be polymerized to polyenes by acyclic diene metathesis. The condensation of α,ω-dienes in presence of a particular metathesis catalyst undergo a polymerization reaction and gives a growing unsaturated polymer chain having specific symmetry and functionality of the monomer.
As the name indicates ADMET is a type of olefin metathesis that involves ends of a long chain. ADMET produce by product which is in gaseous form and escapes from reaction mixture and favor the equilibrium towards polymer product.
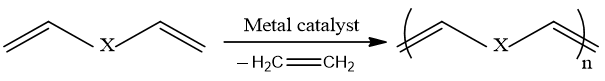
Both cis and trans configuration of double are possible, depends on the identities of monomer.
Polymerization of 1,8-nonadiene: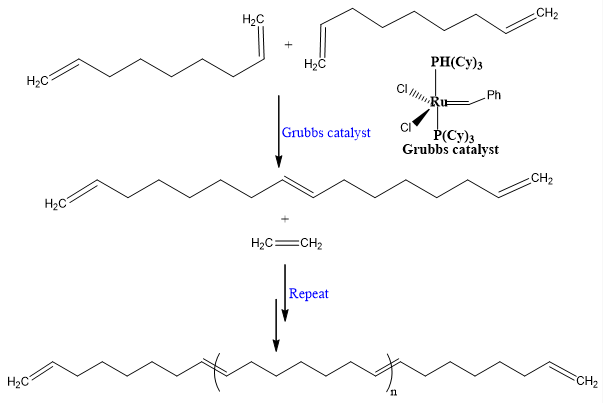
Importance of ADMET:
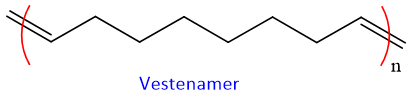
Olefin monomers of many different functional groups are compatible with metathesis reaction. Unreacted double bonds give flexibility for further manipulations. The commercial polymers obtained via olefin metathesis are Vestenamer.
Ziegler-Natta polymerization:
Dienes can be polymerized by a titanium/aluminium catalyst. When alkyl aluminium is treated with titanium compound, an organometallic transition-metal complex is formed Commonly name as Ziegler-Natta catalyst after the name of scientist Ziegler and Natta. This compound can catalyze the polymerization of dienes with remarkable stereoregularity.
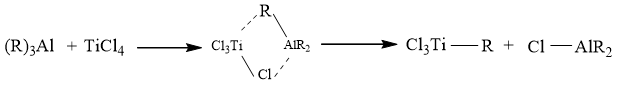
General mechanism of polymerization:
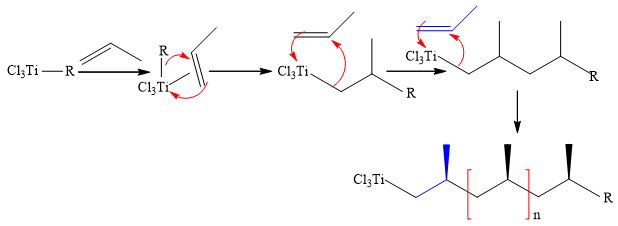
A π-complex is formed between alkyl-Ti σ complex and first molecule of olefin, which then undergo carbo-titanation of π-bond and first C-C bond is formed, tehn second molecule of olefin get inserted by repeating the previous step and polymerization starts. The transformation of a π complex into σ complex is responsible for each new C-C bond formation on coordination sphere of Ti.
Polymerization of isoprene:
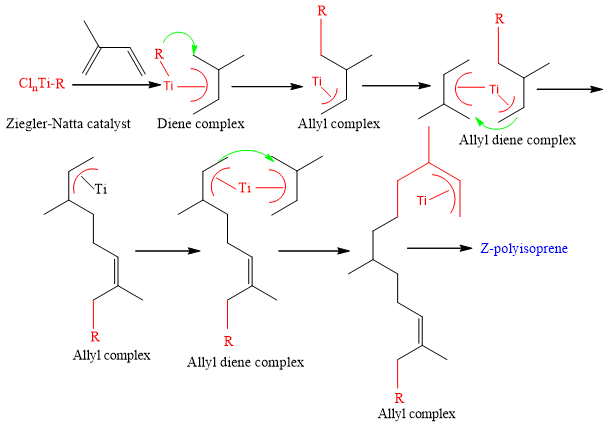
Isoprene (3-methyl-1,3-Butadiene) in presence of Ziegler-Natta catalyst gives all cis- polyisoprene.
Stereochemistry of Ziegler-Natta catalyst:
Polyenes including dienes like isoprene can be polymerized in three different stereo chemical forms, with somewhat different properties and can be prepared by using a particular catalyst. Ziegler- Natta catalysts can form all three configuration i-e Isotactic, Syndiotactic, Atactic. These types are classified on the basis of product formed as a result of polymerization.
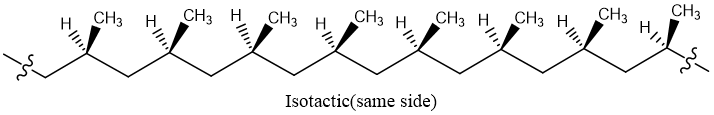
Isotactic:
When all methyl groups lie on the same side of zigzag backbone is called isotactic polymer.
Syndiotactic:
The polymer in which all methyl groups lie on opposite side of zigzag backbone is called syndiotactic polymer.
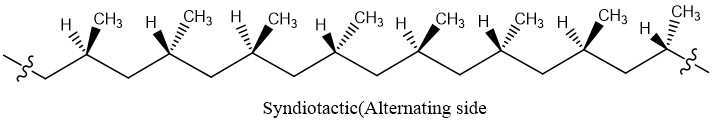
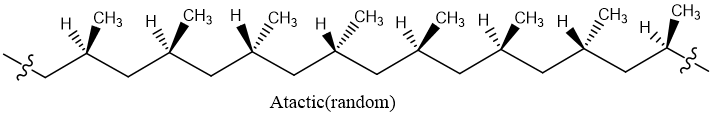
Atactic:
When all methyl groups are randomly oriented is called atactic polymer.
Importance of Ziegler-Natta catalyst:
The field of polymer chemistry is revolutionized after the development of Ziegler-Natta catalyst due to two advantages
 The resultant polymer is linear with no branching
The resultant polymer is linear with no branching Polymers are stereochemically controllable; all three stereochemical forms (Isotactic, Syndiotactic, and Atactic) are possible by using a right catalyst.
Polymers are stereochemically controllable; all three stereochemical forms (Isotactic, Syndiotactic, and Atactic) are possible by using a right catalyst.
