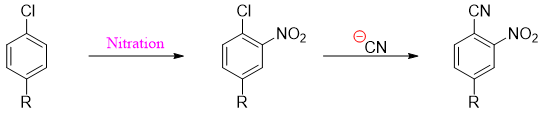
(SnAr) Addition/Elimination Reactions
(SnAr) Addition Elimination Reactions
Benzene ring being electron rich in nature does not reacts with nucleophiles as the pi electron cloud of benzene repels the incoming nucleophile. However, aryl halides containing electron withdrawing (EWG) substituent(s) are poor in electron density thus allowing nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SnAr) reactions to take place. It is important that the EWG must pe present at ortho and para positions to the halogen substituent. The general reaction for SnAr is given below.
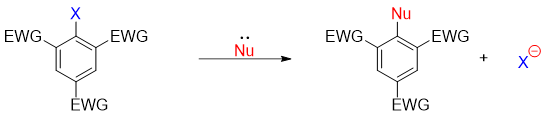
Following are some examples of nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
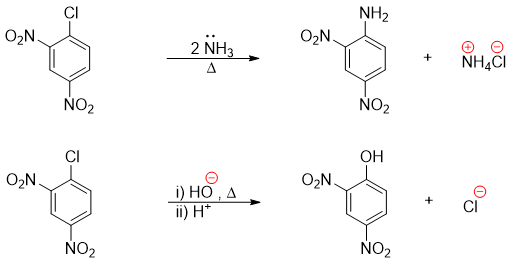
In SnAr reactions the nucleophile adds, and the halogen leaves as a leaving group. Such reactions are not termed as nucleophilic substitution reactions (SN2) because the aryl halide does not obey the geometry for the back side addition of nucleophile as that observed in SN2 reactions. These reactions are neither termed as SN1 reactions.
The SnAr reactions can take place via two different mechanisms i.e., 1) Addition-Elimination mechanism and 2) Elimination-Addition mechanism.
Addition-Elimination mechanism
This mechanism takes place in two steps. In first step the addition of nucleophile takes place followed by second step in which the leaving group eliminates.
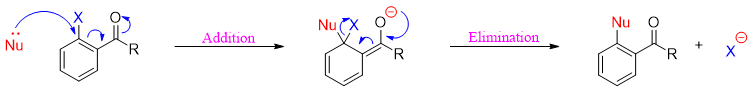
In the first step the addition of nucleophiles generates a negatively charged sigma complex which is stabilized by the electron withdrawing groups present at ortho and para positions.
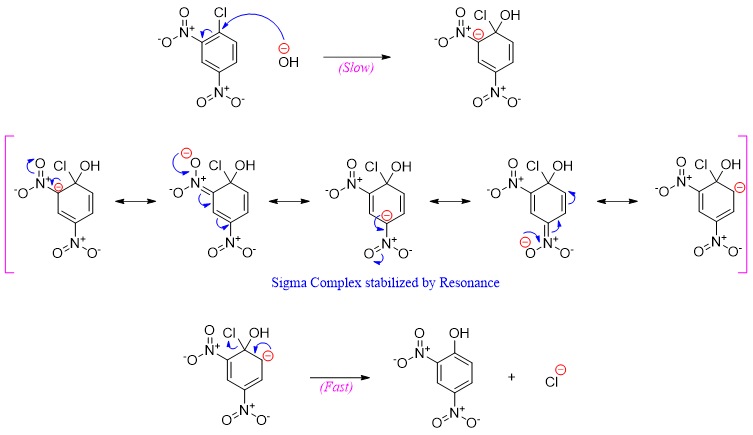
The final product phenol in above mechanism loses proton to base. Hence, once the reaction is completed an acid is added to re-protonate the phenol.
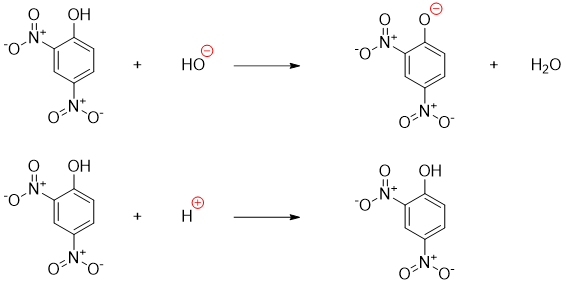
For a typical nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction to take place the nucleophile contains oxygen or nitrogen, or the nucleophile is cyanide, the leaving group is typically halogen and the sigma complex stabilizing electron withdrawing groups present at ortho and para positions are typically nitro group, carbonyl group or cyanide group.
The nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions have many applications. Since EWG groups are meta directing therefore, SnAr reactions are employed to synthesize compounds in which substituents are added at position having EWG at ortho position. In example below, nitro group is added at ortho position to cyanide group (meta directing).