Iodination
Iodination of Benzene
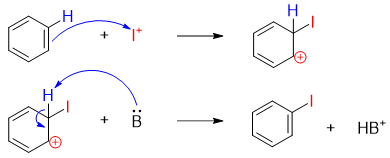
In iodination reaction the hydrogen atom on benzene is replaced by iodine atom via electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
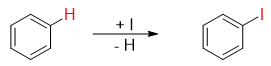
The Iodine molecule is unreactive towards benzene ring thus, oxidizing agents like copper salt (CuCl2), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or nitric acid (HNO3) are added to the reaction.
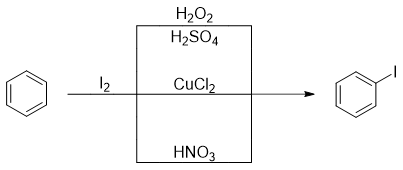
The oxidizing agent is used to oxidize I2 molecule and generate Iodonium ion (I+) which act as electrophile.
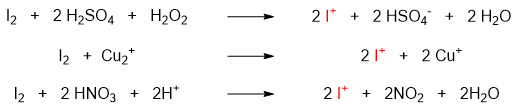
Once the electrophile is generated it is added to benzene ring via electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
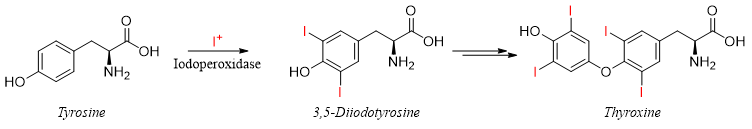
The process of Iodination has many applications including the biosynthesis of thyroxine harmone. Thyroxine produced in thyroid glands increases the rate of metabolism of different biomolecules. The enzyme iodoperoxidase present in thyroid gland uses iodine to convert tyrosine amino acid into thyroxine.
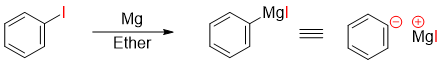
The carbon-iodine bond in iodobenzene is weaker than C-Cl and C-Br bond thus makes it more reactive. Iodobenzene when reacted with magnesium forms phenylmagnesium iodide (Grignard reagent) which is a phenyl anion synthon.
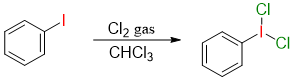
Iodobenezene is also used to prepare Iodobenzene dichloride complex. The complex is synthesized by passing chlorine gas through iodobenzene solution.
Iodobenzene dichloride is used as chlorinating agent and oxidizing agent. In organic synthesis it is employed for the selective chlorination of alkynes and alkenes.
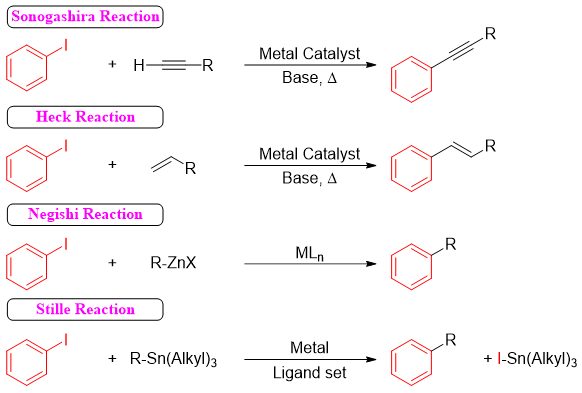
In many metal-catalyzed coupling reactions iodobenzene is used as a substrate. For example.