Properties of Stereoisomers
Properties of Stereoisomers
Physical Properties of Stereoisomers:
Enantiomers have almost the identical properties (boiling points, melting points, densities, solubilities, heat of formations etc.) except for their optical rotation. The enantiomers rotate the plane polarized light in opposite directions. On the other hand, diastereomers have different physical properties. Following table summarizes the physical properties of three stereoisomers and racemic mixture of tartaric acid.
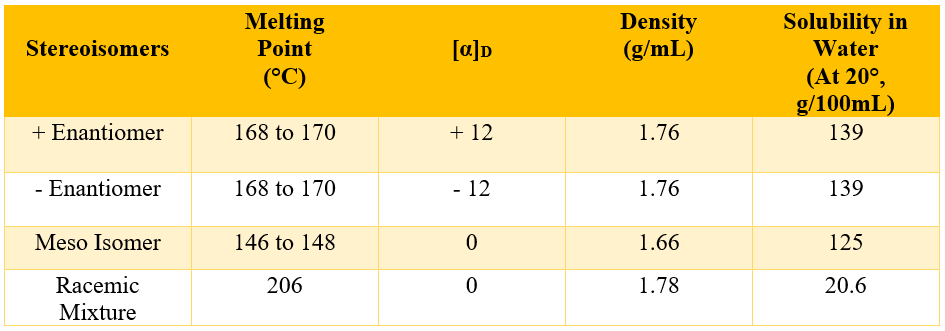
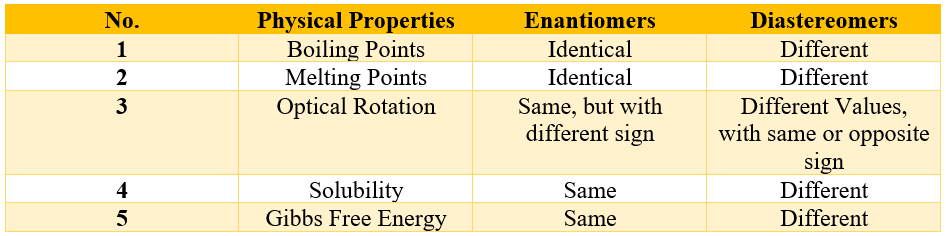
In racemic mixture the two enantiomers are present in equal quantities. It is a 50:50 mixture of both enantiomers. As the two enantiomers are mirror images of each other therefore, they will rotate the plane polarized light in equal extent but with opposite directions hence, cancelling out each other and making the overall optically inactive. This shows that stereoisomers of a single compound can exhibit different physical properties. Enantiomers have almost the same physical properties when measured individually. Following table summarizes the differences and similarities in physical properties of enantiomers and diastereomers.
Biological Properties of Stereoisomers:
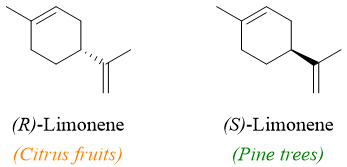
Enantiomers of a compound have the same physical properties, but they usually demonstrate different biological properties. For example, the two enantiomers of Limonene exhibit two different odors. The (S)-Limonene has the odor of pine trees whereas, the (R)-Limonene has the scent of lemons and oranges.
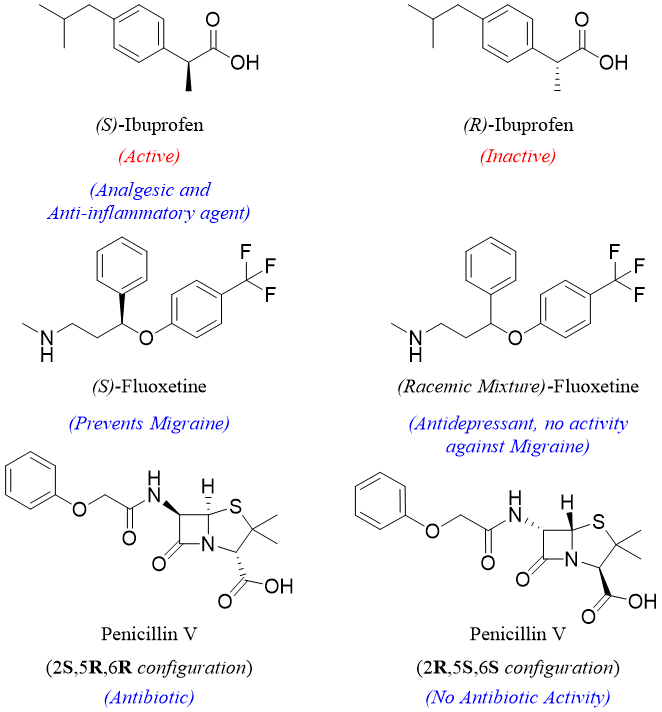
The change in chirality has a dramatic change in biological properties of an optically active molecules found in many drugs. Following enantiomers of different drugs explains the changes in their biological properties.
Different enantiomers have different biological properties because the enantiomers bind to specific receptors of the protein. As the proteins are chiral in nature thus, the receptor binds one enantiomer better than the other enantiomer. Following figure illustrates the binding of two enantiomers to a receptor with specific shape.
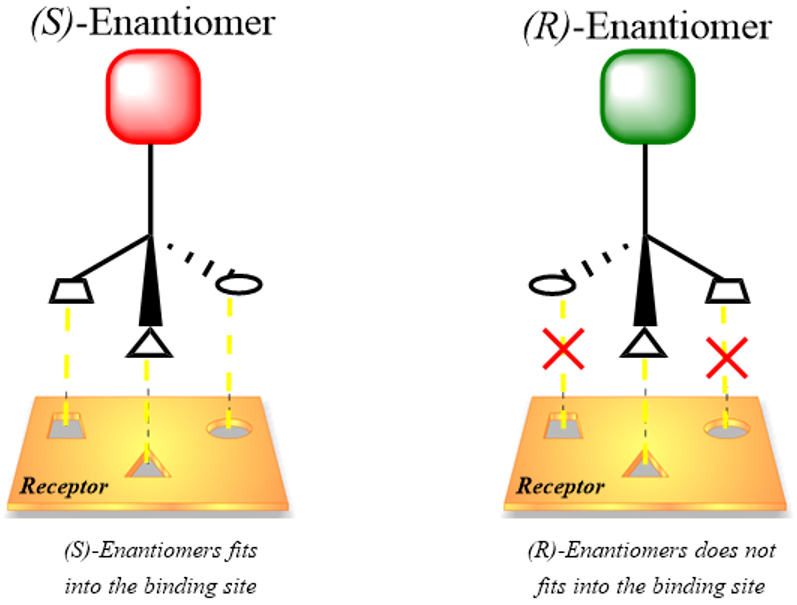
Typically, a receptor recognizes only a single enantiomer, this results in different physiological properties for enantiomers.
Chemical Properties of Stereoisomers:
The stereochemistry of an optically active compound has much impact on different chemical reactions. For example, the E2 elimination reaction takes place when the hydrogen atom and leaving groups are antiperiplanar.

In above example two diastereomers are involved in giving different chemical reactions. In case of enantiomers the results are identical.
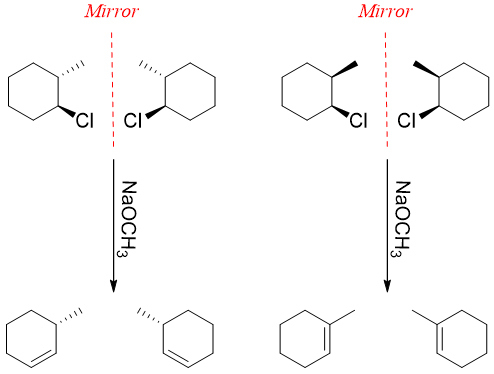
Thus, the enantiomers also have same chemical properties. The enantiomers can give different chemical reactions only if they are reacted with chiral molecules.
